In this article, we are going to implement the Angular(14) state management CRUD example with NgRx(14)Ngrx State Management flow:
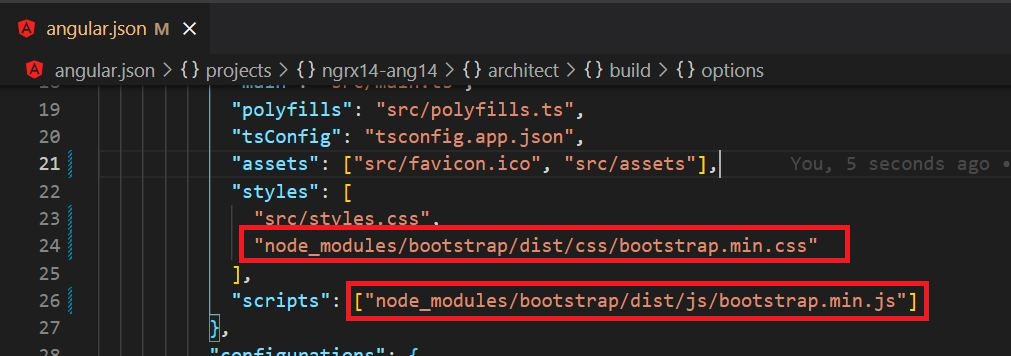
Configure Bootstrap CSS and JS files in 'angular.json'
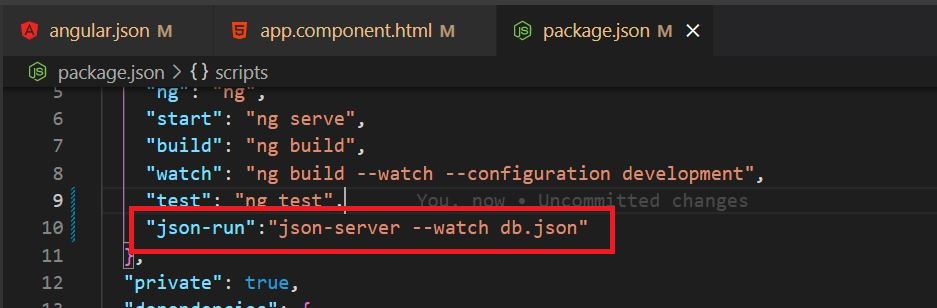
Now go to our angular application and add a command to run the JSON server into the 'package.json' file.Now to invoke the above command, run the below command in the angular application root folder in a terminal window.
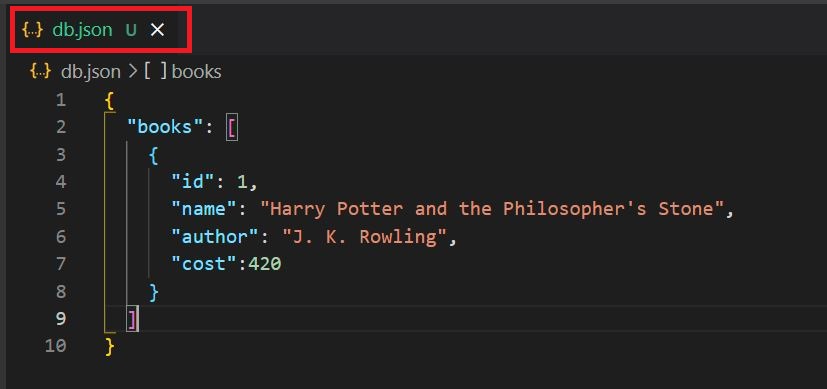
After running the above command for the first time, a 'db.json' file gets created, so this file act as database. So let's add some sample data in the 'db.json' file as below.
Add a component like 'Home' in the 'Books' module.
The 'Effects' are used to invoke the API calls. Let's create a 'Books' effect.
Add the new route in 'books-routing.modulet.ts'.
NgRx Store For State Management:
In an angular application to share consistent data between multiple components, we use NgRx state management. Using NgRx state helps to avoid unwanted API calls, easy to maintain consistent data, etc. The main building blocks for the NgRx store are:
- Actions - NgRx actions represents event to trigger the reducers to save the data into the stores.
- Reducer - Reducer's pure function, which is used to create a new state on data change.
- Store - The store is the model or entity that holds the data.
- Selector - Selector to fetch the slices of data from the store to angular components.
- Effects - Effects deals with external network calls like API. The effect gets executed based the action performed
- The angular component needs data for binding.
- So angular component calls an action that is responsible for invoking the API call.
- After completing the API response will bed passed to the action method that is registered with the reducer for updating the state.
- So to fetch data inside of the store, components call selectors. The selector is a function that can fetch any slice of data from the store.
Create An Angular(14) Application:
Let's create an angular(14) application to accomplish our demo.
Command To Create Angular Application
ng new name_of_your_app
ng new name_of_your_app
Install the bootstrap package
npm install bootstrap
Configure Bootstrap CSS and JS files in 'angular.json'
Add bootstrap NabBar component in 'app.component.html'
<nav class="navbar navbar-expand-lg bg-dark">
<div class="container-fluid">
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">Navbar</a>
</div>
</nav>
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
Setup JSON Server:
Let's set up a fake API by setting up the JSON server in our local machine.
Run the below command to install the JSON server globally onto your local machine.
npm install -g json-server
Now go to our angular application and add a command to run the JSON server into the 'package.json' file.Now to invoke the above command, run the below command in the angular application root folder in a terminal window.
npm run json-run
After running the above command for the first time, a 'db.json' file gets created, so this file act as database. So let's add some sample data in the 'db.json' file as below.
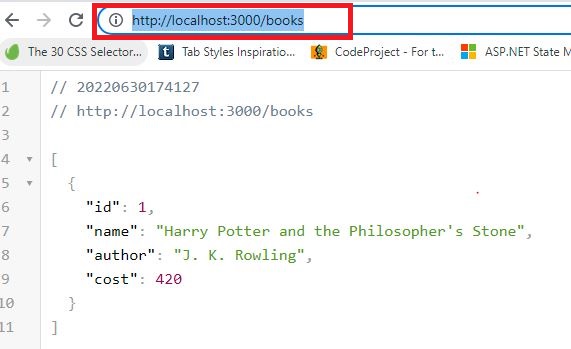
Now access the API endpoint like 'http://localhost:3000/books'.
Create An Angular Feature Module(Ex: Books Module) And A Component(Ex: Home Component):
Let's create a Feature Module or Child Module like 'Books'. So run the below command to generate the module along with the route module
ng generate module books --routing
Add a component like 'Home' in the 'Books' module.
ng generate component books/home
We are going to use the lazy loading technique for the modules. So in 'app-routing.module.ts' define a route for 'Books' module
src/app/app-routing.module.ts:
// existing code hidden for display pupose
const routes: Routes = [
{
path: '',
loadChildren: () =>
import('./books/books.module').then((b) => b.BooksModule),
},
];
Now define a route for the 'Home' component in the 'Book' routing module.src/app/books/books-routing.module.ts:
// existing code hidden for display purpose
import { HomeComponent } from './home/home.component';
const routes: Routes = [
{
path: '',
component: HomeComponent,
},
];
Install NgRx Packages:
Install the '@ngrx/store' package
ng add @ngrx/store@latest
Install the '@ngrx/effects' package
ng add @ngrx/effects@latest
Install the '@ngrx/store-devtools' package
ng add @ngrx/store-devtools@latest
Create A Feature Store(Ex: Books Module State Management Store):
Create A Feature Store or Child Store for the 'Books' module.
Let's create the 'Books' entity file
ng generate interface books/store/books
src/app/books/store/books.ts:
export interface Books {
id: number;
name: string;
author: string;
cost: number;
}
- Here 'Books' model represents the type of the API response and the type of our 'Store'.
ng generate class books/store/books.reducer
src/app/books/store/books.reducer.ts:
import { createReducer } from "@ngrx/store";
import { Books } from "../store/books";
export const initialState: ReadonlyArray<Books> = [];
export const bookReducer = createReducer(
initialState
);
- (Line: 4) Empty array assigned as initial data of our store.
- (Line: 6) Using 'createReducer' that loads from '@ngrx/store' we created our 'bookReducers' by sending 'initialState' as an input parameter.
ng generate class books/store/books.selector
src/app/books/store/books.selector.ts:
import { createFeatureSelector } from '@ngrx/store';
import { Books } from './books';
export const selectBooks = createFeatureSelector<Books[]>('mybooks');
- The 'createFeatureSelector' loads from the '@ngrx/store'. The 'createFeatureSelector' is used to fetch all the data from our feature module(eg: 'Books' module). Here the name of our selector 'mybooks' must be used to register the 'bookReducer' into the 'books.modulet.ts' to register the feature store or child store.
src/app/books/book.module.ts:
// existing code hidden for display purpose
import { StoreModule } from '@ngrx/store';
import { bookReducer } from './stroe/books.reducer';
@NgModule({
imports: [
StoreModule.forFeature('mybooks', bookReducer),
],
})
export class BooksModule {}
The 'Actions' represents the events raised by the component to communicate either with reducers or effects to update the data to store. Let's create a 'Books' action.
ng generate class books/store/books.action
The 'Effects' are used to invoke the API calls. Let's create a 'Books' effect.
ng generate class books/store/books.effect
src/app/books/store/books.effect.ts:
import { Injectable } from "@angular/core";
@Injectable()
export class BooksEffect {
}
- The 'BooksEffect' class is just an injectable service. In the next steps, we write actions and trigger effects to invoke the API calls in this service.
src/app/books/books.module.ts:
// existing code hidden for display purpose
import { EffectsModule } from '@ngrx/effects';
import { BooksEffect } from './store/books.effect';
@NgModule({
imports: [
EffectsModule.forFeature([BooksEffect])
],
})
export class BooksModule {}
Finally, our feature store('Books' store) files look as below.
Create A Service(Ex: BooksService) File:
To implement our API calls let's create a service like 'BooksService'.
ng generate service books/books
src/app/books/books.service.ts:
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { HttpClient } from '@angular/common/http';
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root',
})
export class BooksService {
constructor(private http: HttpClient) {}
}
Now register 'HttpClientModule' in 'AppModule'.src/app/app.module.ts:
// existing code hidden for display purpose
import { HttpClientModule } from '@angular/common/http';
@NgModule({,
imports: [
HttpClientModule
]
})
export class AppModule { }
Implement Read Operation:
Let's implement read operation which means need to invoke the API, then store the API response in the state management store, then the component continuously listens for new state generation and fetches the new state data for UI binding.
Let's implement the logic to call API in 'BookService'.
src/app/books/books.service.ts:
get() {
return this.http.get<Books[]>('http://localhost:3000/books');
}
Let's update our 'Books' action file as below.
src/app/books/store/books.action.ts:
import { createAction, props } from '@ngrx/store';
import { Books } from './books';
export const invokeBooksAPI = createAction(
'[Books API] Invoke Books Fetch API'
);
export const booksFetchAPISuccess = createAction(
'[Books API] Fetch API Success',
props<{ allBooks: Books[] }>()
);
- The 'createAction' loads from the '@ngrx/store'
- The name of the action is a simple string but it recommends following rules like '[Source] Event or Action To Do'(eg:'[Books API]' is the source, 'Invoke Books Fetch API' is event or action)
- To send input parameters to the action, then the parameter needs to be wrapped with 'props'. The 'props' loads from the '@ngrx/store'.
- (Line: 4-6) Defined an action 'invokeBooksAPI', this action going to invoke the API call.
- (Line: 9-11) Defined an action 'bookFetchAPISuccess', this action method invoked after the API call is successful, this action method saves the API response into the store.
src/app/books/store/books.effect.ts:
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { Actions, createEffect, ofType } from '@ngrx/effects';
import { select, Store } from '@ngrx/store';
import { EMPTY, map, mergeMap, withLatestFrom } from 'rxjs';
import { BooksService } from '../books.service';
import { booksFetchAPISuccess, invokeBooksAPI } from './books.action';
import { selectBooks } from './books.selector';
@Injectable()
export class BooksEffect {
constructor(
private actions$: Actions,
private booksService: BooksService,
private store: Store
) {}
loadAllBooks$ = createEffect(() =>
this.actions$.pipe(
ofType(invokeBooksAPI),
withLatestFrom(this.store.pipe(select(selectBooks))),
mergeMap(([, bookformStore]) => {
if (bookformStore.length > 0) {
return EMPTY;
}
return this.booksService
.get()
.pipe(map((data) => booksFetchAPISuccess({ allBooks: data })));
})
)
);
}
- (Line: 12) Injected the 'Actions' service that loads from the '@ngrx/effects'
- (Line: 14) The 'Store'(our 'Books' store) injected that loads from the '@ngrx/store'
- (Line: 17) The 'createEffect()' that loads from the '@ngrx/effects' helps to create the ngrx effects.
- (Line: 19) The 'ofType' loads from the '@ngrx/effects'. It takes action(eg: invokeBooksAPI) as input parameter. It allows the execution-only the action that registered with got invoked.
- (Line: 20) The 'withLatestFrom' loads from the 'rxjs'. It outputs the latest result of an observable. Here 'this.store.pipe(select(selectBooks))' trying to fetch the data from the store if already exist.
- (Line: 21) The 'mergeMap' loads from the 'rxjs'. Here are 2 input parameters we are reading inside of the 'mergeMap'. The first input parameter is undefined because 'ofType' observable has a void action method and the second input parameter comes from the 'withLatesFrom'.
- (Line: 22-24) If the data already exists in the ngrx store, then return 'EMTY' observable.
- (Line: 25-27) If the data do not already exist, thin invoke the API call, on receiving a successful response save it store by calling the 'bookFetchAPISuccess'(action).
src/app/books/store/books.reducer.ts:
import { createReducer, on } from '@ngrx/store';
import { Books } from './books';
import { booksFetchAPISuccess } from './books.action';
export const initialState: ReadonlyArray<Books> = [];
export const bookReducer = createReducer(
initialState,
on(booksFetchAPISuccess, (state, { allBooks }) => {
return allBooks;
})
);
- (Line: 9-10)In reducer to register action, we have to use 'on' that loads from the '@ngrx/store'. Here 'on' has an arrow function as the second parameter. The arrow function contains 2 parameters, first, the param is the existing store state, and the second param is the action(eg: boooksFetchAPISuccess) payload(API payload)
src/app/books/home/home.component.ts:
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { select, Store } from '@ngrx/store';
import { invokeBooksAPI } from '../store/books.action';
import { selectBooks } from '../store/books.selector';
@Component({
selector: 'app-home',
templateUrl: './home.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./home.component.css'],
})
export class HomeComponent implements OnInit {
constructor(private store: Store) {}
books$ = this.store.pipe(select(selectBooks));
ngOnInit(): void {
this.store.dispatch(invokeBooksAPI());
}
}
- (Line: 12) Inject the 'Store' loads from the '@ngrx/store'.
- (Line: 13) Declared the 'books$' observable that listens for the changes from the store. Here we use 'selectBooks' selector to fetch all the data from the store.
- (Line: 16) Here invoking the 'invokeBooksAPI' action method which will invoke ngrx effect that invokes an API call.
<div class="container mt-2">
<div class="row row-cols-1 row-cols-md-3 g-4">
<div class="col" *ngFor="let book of books$ | async">
<div class="card">
<div class="card-body">
<h5 class="card-title">{{ book.name }}</h5>
</div>
<ul class="list-group list-group-flush">
<li class="list-group-item">{{ book.author }}</li>
<li class="list-group-item">${{ book.cost }}</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
- Here looping our collection of data that loaded from the store.
Create Shared/Global State Management Store:
Sometimes we want to share some data globally through the application, so let's try to implement a shared/global state management store.
Let's create an entity or model for a global state management store.
ng generate interface shared/store/appstate
src/app/shared/store/appstate.ts:
export interface Appstate {
apiStatus: string;
apiResponseMessage: string;
}
- Here created properties like 'apiStatus'(eg: 'Sucess', or 'Failed'), 'apiResponseMessage'(to store the any server-side exception message).
ng generate class shared/store/app.action
src/app/shared/stroe/app.action.ts:
import { createAction, props } from "@ngrx/store";
import { Appstate } from "./appstate";
export const setAPIStatus = createAction(
'[API] success or failure status',
props<{apiStatus: Appstate}>()
);
- Here created an action method that raised for API success or Failure message.
ng generate class shared/store/app.reducer
src/app/shared/store/app.reduce.ts:
import { createReducer, on } from '@ngrx/store';
import { setAPIStatus } from './app.action';
import { Appstate } from './appstate';
export const initialState: Readonly<Appstate> = {
apiResponseMessage: '',
apiStatus: '',
};
export const appReducer = createReducer(
initialState,
on(setAPIStatus, (state, { apiStatus }) => {
return {
...state,
...apiStatus
};
})
);
- (Line: 5-8) Initialized the 'initialState'.
- (Line: 10-18) created the 'appReducer'. Registered the 'setAPIStatus' action for generating the new state.
src/app/shared/store/app.selector.ts:
import { createFeatureSelector } from '@ngrx/store';
import { Appstate } from './appstate';
export const selectAppState = createFeatureSelector<Appstate>('appState');
Now let's register 'appState'(name of the selector) and 'appReducer' in 'AppModule'.src/app/app.module.ts:
// existing code hidden for display purpose
import { StoreModule } from '@ngrx/store';
import { appReducer } from './shared/store/app.reducer';
@NgModule({
imports: [
StoreModule.forRoot({ appState: appReducer })
]
})
export class AppModule { }
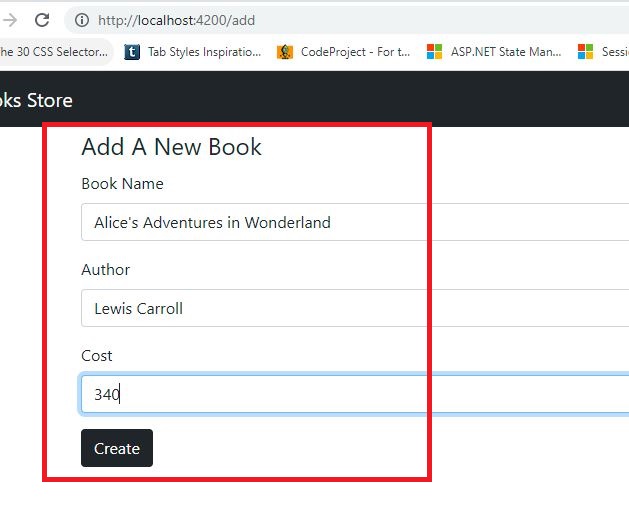
Create 'Add' Component:
Create a new angular component like 'Add'.
ng generate component books/add
Add the new route in 'books-routing.modulet.ts'.
src/app/books/books-routing.module.ts:
import { AddComponent } from './add/add.component';
//existing code hidden for display purpose
const routes: Routes = [
{
path: 'add',
component: AddComponent,
},
];
Implement Create Operation:
Let's implement the 'Create' operation in our sample.
Let's add the create API call in the 'books.service.ts'
src/app/books/books.service.ts:
create(payload: Books) {
return this.http.post<Books>('http://localhost:3000/books', payload);
}
Let's create a new action method as below.src/app/books/store/books.action.ts:
export const invokeSaveNewBookAPI = createAction(
'[Books API] Inovke save new book api',
props<{ newBook: Books }>()
);
export const saveNewBookAPISucess = createAction(
'[Books API] save new book api success',
props<{ newBook: Books }>()
);
- The 'invokeSaveNewBookAPI' action method invokes the create API, action has input 'newBook' which will be the payload to API.
- The 'saveNewBookAPISuccess' action method is executed after API success and the newly created record that comes as a response will be saved to the store.
src/app/books/store/books.effect.ts:
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { Actions, createEffect, ofType } from '@ngrx/effects';
import { select, Store } from '@ngrx/store';
import { EMPTY, map, mergeMap, switchMap, withLatestFrom } from 'rxjs';
import { setAPIStatus } from 'src/app/shared/store/app.action';
import { Appstate } from 'src/app/shared/store/appstate';
import { BooksService } from '../books.service';
import {
booksFetchAPISuccess,
invokeBooksAPI,
invokeSaveNewBookAPI,
saveNewBookAPISucess,
} from './books.action';
import { selectBooks } from './books.selector';
@Injectable()
export class BooksEffect {
constructor(
private actions$: Actions,
private booksService: BooksService,
private store: Store,
private appStore: Store<Appstate>
) {}
// existing code hidden for display purpose
saveNewBook$ = createEffect(() => {
return this.actions$.pipe(
ofType(invokeSaveNewBookAPI),
switchMap((action) => {
this.appStore.dispatch(
setAPIStatus({ apiStatus: { apiResponseMessage: '', apiStatus: '' } })
);
return this.booksService.create(action.newBook).pipe(
map((data) => {
this.appStore.dispatch(
setAPIStatus({
apiStatus: { apiResponseMessage: '', apiStatus: 'success' },
})
);
return saveNewBookAPISucess({ newBook: data });
})
);
})
);
});
}
- (Line: 22)Injected 'Store<AppState>' shared store.
- (Line: 27) Created a new effect 'saveNewBook$' to invoke the API.
- (Line: 30) The input parameter to the 'switchMap' is an instance of 'action' that contains our payload to send to the server.
- (Line: 31-33) Before calling the API, we are resetting the 'apiStatus' & 'apiResponseMessage' values of the global store by invoking the 'setAPIStatus'.
- (Line: 36-40) After API cal successful here setting the 'apiStatus' to 'success'.
- (Line: 41) The 'saveNewBookAPISuccess' action updates the state of the store with the newly created record.
src/app/books/store/books.reducer.ts:
import { createReducer, on } from '@ngrx/store';
import { Books } from './books';
import { booksFetchAPISuccess, saveNewBookAPISucess } from './books.action';
export const initialState: ReadonlyArray<Books> = [];
export const bookReducer = createReducer(
initialState,
on(booksFetchAPISuccess, (state, { allBooks }) => {
return allBooks;
}),
on(saveNewBookAPISucess, (state, { newBook }) => {
let newState = [...state];
newState.unshift(newBook);
return newState;
})
);
- (Line: 12-16) Here we generate the new state along with by adding the newly created record.
src/app/books/add/add.component.ts:
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { Router } from '@angular/router';
import { select, Store } from '@ngrx/store';
import { setAPIStatus } from 'src/app/shared/store/app.action';
import { selectAppState } from 'src/app/shared/store/app.selector';
import { Appstate } from 'src/app/shared/store/appstate';
import { Books } from '../store/books';
import { invokeSaveNewBookAPI } from '../store/books.action';
@Component({
selector: 'app-add',
templateUrl: './add.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./add.component.css'],
})
export class AddComponent implements OnInit {
constructor(
private store: Store,
private appStore: Store<Appstate>,
private router: Router
) {}
bookForm: Books = {
id: 0,
author: '',
name: '',
cost: 0,
};
ngOnInit(): void {}
save() {
this.store.dispatch(invokeSaveNewBookAPI({ newBook: this.bookForm }));
let apiStatus$ = this.appStore.pipe(select(selectAppState));
apiStatus$.subscribe((apState) => {
if (apState.apiStatus == 'success') {
this.appStore.dispatch(
setAPIStatus({ apiStatus: { apiResponseMessage: '', apiStatus: '' } })
);
this.router.navigate(['/']);
}
});
}
}
- (Line: 17) The 'Store' injected here is our feature module(book module) store.
- (Line: 18) The 'Store<AppState>' injected here is our shared or global store.
- (Line: 19) Injected 'Router' service that loads from the '@angular/router'.
- (Line: 22-27) The 'bookFrom' object is initialized to use for form binding.
- (Line: 32) Invoking the save API effect by calling the 'invokeSaveNewBookAPI' action.
- (Line: 34-40) Listening for data changes in the global store. So here we confirm that our save API is successful based on the 'apiStatus' value and then navigate back to 'HomeComponent'.
<div class="container">
<legend>Add A New Book</legend>
<div class="mb-3">
<label for="txtBookName" class="form-label">Book Name</label>
<<
type="text"
[(ngModel)]="bookForm.name"
class="form-control"
id="txtBookName"
/>
</div>
<div class="mb-3">
<label for="txtAuthor" class="form-label">Author</label>
<<
type="text"
[(ngModel)]="bookForm.author"
class="form-control"
id="txtAuthor"
/>
</div>
<div class="mb-3">
<label for="txtCost" class="form-label">Cost</label>
<<
type="number"
[(ngModel)]="bookForm.cost"
class="form-control"
id="txtCost"
/>
</div>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-dark" (click)="save()">Create</button>
</div>
Now let's import the 'FormModule' into the 'books.module.ts'.src/app/books/books.module.ts:
import { FormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
// existing code hidden for display purpose
@NgModule({
imports: [
FormsModule
],
})
export class BooksModule {}
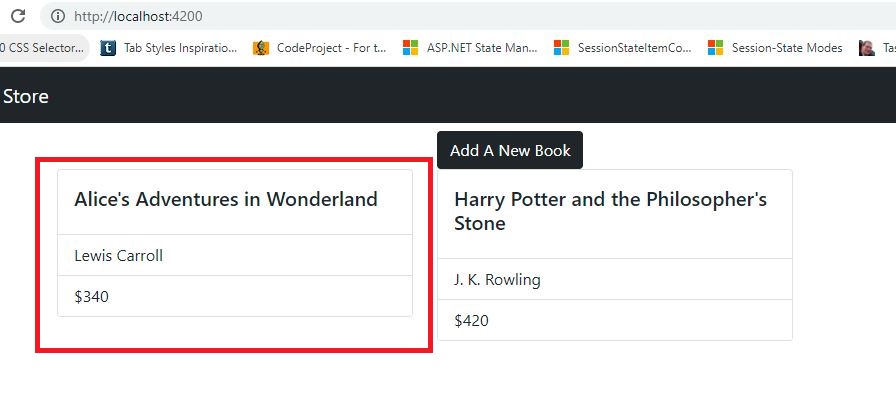
Now on 'home.component.html' add a button to navigate the 'AddComponent.'.src/app/books/home/home.component.html:
<div class="row"> <div class="col col-md-4 offset-md-4"> <a routerLink="/add" class="btn btn-dark">Add A New Book</a> </div> </div>step1:step 2:step3:
Create 'Edit' Component:
Let's create a new angular component like 'Edit'.
ng generate component books/add
Now configure the 'Edit' component route in 'books-routing.module.ts'.
src/app/books/books-routing.module.ts:
import { EditComponent } from './edit/edit.component';
// existing code hidden for display purpose
const routes: Routes = [
{
path: 'edit/:id',
component: EditComponent,
},
];
- Here ':id' is a dynamic path placeholder.
Implement Update Operation:
Let's implement the 'Update' operation in our sample using ngrx store.
Let's add the update API call in our 'books.service.ts'.
src/app/books/books.service.ts:
update(payload: Books) {
return this.http.put<Books>(
`http://localhost:3000/books/${payload.id}`,
payload
);
}
Let's create a new action method as below.src/app/books/store/books.action.ts:
export const invokeUpdateBookAPI = createAction(
'[Books API] Inovke update book api',
props<{ updateBook: Books }>()
);
export const updateBookAPISucess = createAction(
'[Books API] update book api success',
props<{ updateBook: Books }>()
);
- The 'invokeUpdateBookAPI' action method trigger a ngrx effects that execute the update API call.
- The 'updateBookAPISuccess' action method gets invoked on the success of the update API call. The 'updateBookAPISuccess' invokes the reducer to create a new store state with updated data.
src/app/books/store/books.effects.ts:
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { Actions, createEffect, ofType } from '@ngrx/effects';
import { select, Store } from '@ngrx/store';
import { EMPTY, map, mergeMap, switchMap, withLatestFrom } from 'rxjs';
import { setAPIStatus } from 'src/app/shared/store/app.action';
import { Appstate } from 'src/app/shared/store/appstate';
import { BooksService } from '../books.service';
import {
booksFetchAPISuccess,
invokeBooksAPI,
invokeSaveNewBookAPI,
invokeUpdateBookAPI,
saveNewBookAPISucess,
updateBookAPISucess,
} from './books.action';
import { selectBooks } from './books.selector';
@Injectable()
export class BooksEffect {
constructor(
private actions$: Actions,
private booksService: BooksService,
private store: Store,
private appStore: Store<Appstate>
) {}
// existing code hidden for display purpose
updateBookAPI$ = createEffect(() => {
return this.actions$.pipe(
ofType(invokeUpdateBookAPI),
switchMap((action) => {
this.appStore.dispatch(
setAPIStatus({ apiStatus: { apiResponseMessage: '', apiStatus: '' } })
);
return this.booksService.update(action.updateBook).pipe(
map((data) => {
this.appStore.dispatch(
setAPIStatus({
apiStatus: { apiResponseMessage: '', apiStatus: 'success' },
})
);
return updateBookAPISucess({ updateBook: data });
})
);
})
);
});
}
Let's update our reducer to use 'updateBookAPISuccess' action method for updating the store data.src/app/books/store/books.reducer.ts:
import { createReducer, on } from '@ngrx/store';
import { Books } from './books';
import { booksFetchAPISuccess, saveNewBookAPISucess, updateBookAPISucess } from './books.action';
export const initialState: ReadonlyArray<Books> = [];
// existing code hidden for display purpose
export const bookReducer = createReducer(
initialState,
on(updateBookAPISucess, (state, { updateBook }) => {
let newState = state.filter((_) => _.id != updateBook.id);
newState.unshift(updateBook);
return newState;
})
);
Let's create a new selector that fetches data by the 'id' value, so this selector will be used to fetch the data to display on the edit form.src/app/books/store/books.selector.ts:
import { createFeatureSelector, createSelector } from '@ngrx/store';
import { Books } from './books';
export const selectBooks = createFeatureSelector<Books[]>('mybooks');
export const selectBookById = (bookId: number) =>
createSelector(selectBooks, (books: Books[]) => {
var bookbyId = books.filter((_) => _.id == bookId);
if (bookbyId.length == 0) {
return null;
}
return bookbyId[0];
});
- Here 'createSelector' is used to fetch the slice of data from the ngrx store. The 'createSelector' loads from the '@ngrx/store'. The 'createSelector' doesn't support input parameters, so to pass parameters we will create an arrow function and inside of it we will return 'createSelector'.
- (Line: 6-13) Creating a selector like 'selectBookByid' that fetches the selected data from the ngrx store.
src/app/books/edit/edit.component.ts:
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { ActivatedRoute, Router } from '@angular/router';
import { select, Store } from '@ngrx/store';
import { switchMap } from 'rxjs';
import { setAPIStatus } from 'src/app/shared/store/app.action';
import { selectAppState } from 'src/app/shared/store/app.selector';
import { Appstate } from 'src/app/shared/store/appstate';
import { Books } from '../store/books';
import { invokeUpdateBookAPI } from '../store/books.action';
import { selectBookById } from '../store/books.selector';
@Component({
selector: 'app-edit',
templateUrl: './edit.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./edit.component.css'],
})
export class EditComponent implements OnInit {
constructor(
private route: ActivatedRoute,
private router: Router,
private store: Store,
private appStore: Store<Appstate>
) {}
bookForm: Books = {
id: 0,
author: '',
name: '',
cost: 0,
};
ngOnInit(): void {
let fetchData$ = this.route.paramMap.pipe(
switchMap((params) => {
var id = Number(params.get('id'));
return this.store.pipe(select(selectBookById(id)));
})
);
fetchData$.subscribe((data) => {
if (data) {
this.bookForm = { ...data };
}
else{
this.router.navigate(['/']);
}
});
}
udapte() {
this.store.dispatch(
invokeUpdateBookAPI({ updateBook: { ...this.bookForm } })
);
let apiStatus$ = this.appStore.pipe(select(selectAppState));
apiStatus$.subscribe((apState) => {
if (apState.apiStatus == 'success') {
this.appStore.dispatch(
setAPIStatus({ apiStatus: { apiResponseMessage: '', apiStatus: '' } })
);
this.router.navigate(['/']);
}
});
}
}
- (Line: 19&20) Injected the 'ActivatedRoute', 'Router' that loads from the '@angular/router'
- (Line: 21) Injected the 'Store'(Books store) that loads from the '@ngrx/store'
- (Line: 22) Injected the 'Store<AppState>' that is the shared/global store of our application.
- (Line: 25) The 'bookForm' variable declared will be used to bind as a model for the edit form.
- (Line: 35) Here fetching the edit item 'id' value from the route.
- (Line: 36) Invoking the 'selectBookById' selector to fetch data from the store.
- (Line: 39-46) If the record to edit exist in the store, then will assign data to 'bookFrom' variable so that data gets populated on the edit form. If the record does not exist in the store then we navigate back to the 'HomeComponent'.
- (Line: 50-52) Invoking the 'invokeUpdateBookAPI' action method that will trigger the ngrx effect that contains logic to invoke the update API call. Here the 'invokeUpdateBookAPI', we pass our form data as payload.
- (Line: 53-61) Here checking the 'apiStatus' value to check whether our update is successful or not.
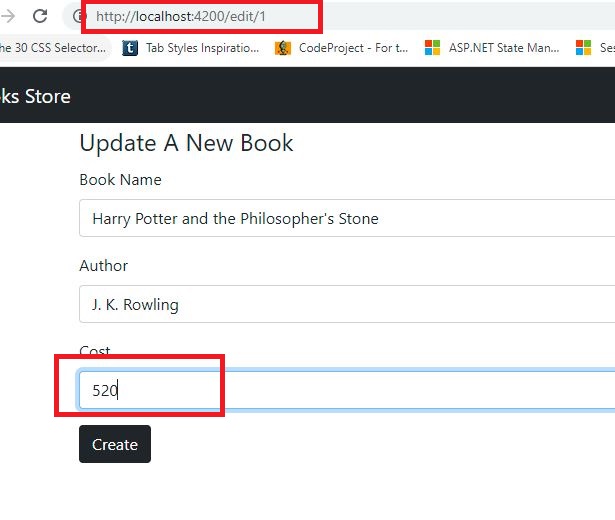
<div class="container">
<legend>Update A New Book</legend>
<div class="mb-3">
<label for="txtBookName" class="form-label">Book Name</label>
<input
type="text"
[(ngModel)]="bookForm.name"
class="form-control"
id="txtBookName"
/>
</div>
<div class="mb-3">
<label for="txtAuthor" class="form-label">Author</label>
<input
type="text"
[(ngModel)]="bookForm.author"
class="form-control"
id="txtAuthor"
/>
</div>
<div class="mb-3">
<label for="txtCost" class="form-label">Cost</label>
<input
type="number"
[(ngModel)]="bookForm.cost"
class="form-control"
id="txtCost"
/>
</div>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-dark" (click)="udapte()">Create</button>
</div>
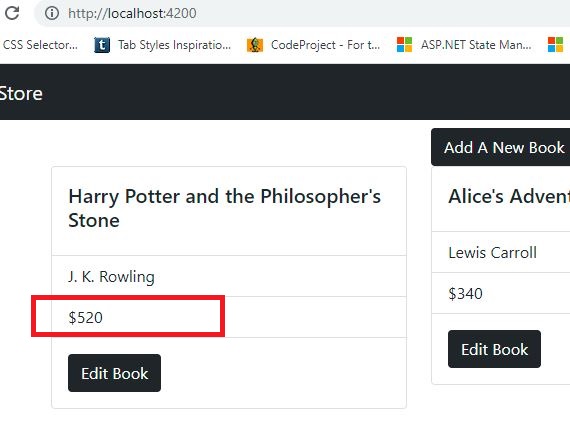
Add the 'Edit' button on the 'home.component.html'. Inside of the bootstrap card component add the below html.src/app/books/home/home.component.html:
<div class="card-body"> <a [routerLink]="['/edit', book.id]" class="btn btn-dark">Edit Book</a> </div>step1
step2:
step3:Implement Delete Operation:
Let's add delete API call in 'books.service.ts'.
src/app/books/books.service.ts:
delete(id: number) {
return this.http.delete(`http://localhost:3000/books/${id}`);
}
Let's add a new action method in 'books.action.ts'.src/app/books/store/books.action.ts:
export const invokeDeleteBookAPI = createAction(
'[Books API] Inovke delete book api',
props<{id:number}>()
);
export const deleteBookAPISuccess = createAction(
'[Books API] deleted book api success',
props<{id:number}>()
);
- The 'invokeDeleteBookAPI' action method triggers ngrx effect that executes delete API.
- The 'deleteBookAPISuccess' action invoked on delete API success. The 'deleteBookAPISuccess' is used by the reducer to remove the item from the store state.
Let's add the delete effect for invoking the delete API call.
src/app/books/store/books.effect.ts:
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { Actions, createEffect, ofType } from '@ngrx/effects';
import { select, Store } from '@ngrx/store';
import { EMPTY, map, mergeMap, switchMap, withLatestFrom } from 'rxjs';
import { setAPIStatus } from 'src/app/shared/store/app.action';
import { Appstate } from 'src/app/shared/store/appstate';
import { BooksService } from '../books.service';
import {
booksFetchAPISuccess,
deleteBookAPISuccess,
invokeBooksAPI,
invokeDeleteBookAPI,
invokeSaveNewBookAPI,
invokeUpdateBookAPI,
saveNewBookAPISucess,
updateBookAPISucess,
} from './books.action';
import { selectBooks } from './books.selector';
@Injectable()
export class BooksEffect {
constructor(
private actions$: Actions,
private booksService: BooksService,
private store: Store,
private appStore: Store<Appstate>
) {}
deleteBooksAPI$ = createEffect(() => {
return this.actions$.pipe(
ofType(invokeDeleteBookAPI),
switchMap((actions) => {
this.appStore.dispatch(
setAPIStatus({ apiStatus: { apiResponseMessage: '', apiStatus: '' } })
);
return this.booksService.delete(actions.id).pipe(
map(() => {
this.appStore.dispatch(
setAPIStatus({
apiStatus: { apiResponseMessage: '', apiStatus: 'success' },
})
);
return deleteBookAPISuccess({ id: actions.id });
})
);
})
);
});
}
Let's update the reducer as below.
src/app/books/store/books.reducer.ts:
import { createReducer, on } from '@ngrx/store';
import { Books } from '../books';
import {
booksFetchAPISuccess,
deleteBookAPISuccess,
saveNewBookAPISucess,
updateNewBookAPISucess,
} from './books.action';
export const initialState: ReadonlyArray<Books> = [];
export const booksReducer = createReducer(
initialState,
// existing code hiden for display purpose
on(deleteBookAPISuccess, (state, { id }) => {
let newState =state.filter((_) => _.id != id);
return newState;
})
);
Let's update the 'home.component.ts' as below.src/app/books/home/home.component.ts:
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { select, Store } from '@ngrx/store';
import { setAPIStatus } from 'src/app/shared/store/app.action';
import { selectAppState } from 'src/app/shared/store/app.selector';
import { Appstate } from 'src/app/shared/store/appstate';
import { invokeBooksAPI, invokeDeleteBookAPI } from '../store/books.action';
import { selectBooks } from '../store/books.selector';
declare var window: any;
@Component({
selector: 'app-home',
templateUrl: './home.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./home.component.css'],
})
export class HomeComponent implements OnInit {
constructor(private store: Store, private appStore: Store<Appstate>) {}
books$ = this.store.pipe(select(selectBooks));
deleteModal: any;
idToDelete: number = 0;
ngOnInit(): void {
this.deleteModal = new window.bootstrap.Modal(
document.getElementById('deleteModal')
);
this.store.dispatch(invokeBooksAPI());
}
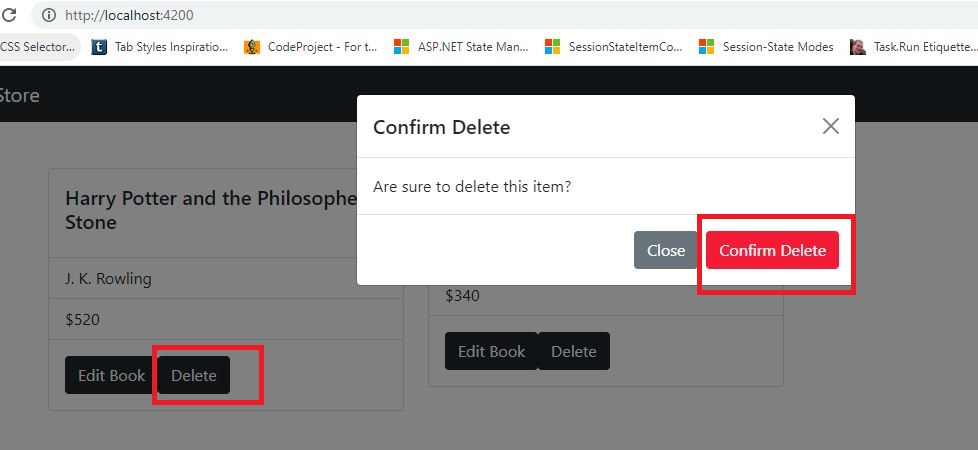
openDeleteModal(id: number) {
this.idToDelete = id;
this.deleteModal.show();
}
delete() {
this.store.dispatch(
invokeDeleteBookAPI({
id: this.idToDelete,
})
);
let apiStatus$ = this.appStore.pipe(select(selectAppState));
apiStatus$.subscribe((apState) => {
if (apState.apiStatus == 'success') {
this.deleteModal.hide();
this.appStore.dispatch(
setAPIStatus({ apiStatus: { apiResponseMessage: '', apiStatus: '' } })
);
}
});
}
}
- (Line: 21) Declare variable 'deleteModal' that will hold the instance of the bootstrap modal.
- (Line: 22) Declare variable 'idDelete' used to assign the record 'id' that needs to be deleted.
- (Line: 25-27) Assigned the bootstrap modal instance to the 'deleteModal'.
- (Line: 34) Opening the delete confirmation modal popup.
- (Line: 38-42) Invoked the 'invokeDeleteBookAPI' action method.
<div class="container mt-2">
<div class="row">
<div class="col col-md-4 offset-md-4">
<a routerLink="/add" class="btn btn-dark">Add A New Book</a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="row row-cols-1 row-cols-md-3 g-4">
<div class="col" *ngFor="let book of books$ | async">
<div class="card">
<!-- <img src="/assets/book.png" class="card-img-top" alt="..." /> -->
<div class="card-body">
<h5 class="card-title">{{ book.name }}</h5>
</div>
<ul class="list-group list-group-flush">
<li class="list-group-item">{{ book.author }}</li>
<li class="list-group-item">${{ book.cost }}</li>
</ul>
<div class="card-body">
<a [routerLink]="['/edit', book.id]" class="btn btn-dark"
>Edit Book</a
>
<button class="btn btn-dark" (click)="openDeleteModal(book.id)">
Delete
</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<!-- Modal -->
<div class="modal fade" id="deleteModal" tabindex="-1" aria-labelledby="exampleModalLabel" aria-hidden="true">
<div class="modal-dialog">
<div class="modal-content">
<div class="modal-header">
<h5 class="modal-title" id="exampleModalLabel">Confirm Delete</h5>
<button type="button" class="btn-close" data-bs-dismiss="modal" aria-label="Close"></button>
</div>
<div class="modal-body">
Are sure to delete this item?
</div>
<div class="modal-footer">
<button type="button" class="btn btn-secondary" data-bs-dismiss="modal">Close</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-danger" (click)="delete()">Confirm Delete</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
- (Line: 22) Added the 'Delete' button.
- (Line: 33-49) Render the bootstrap modal HTML.
Support Me!
Buy Me A Coffee
PayPal Me
Video Session:
Wrapping Up:
Hopefully, I think this article delivered some useful information on Angular 14 State Management CRUD example with NgRx(14). using I love to have your feedback, suggestions, and better techniques in the comment section below.
.png)
-2.jpg)



Excellent Tutorial. Thank you, Naveen.
ReplyDeleteOne of the best tutorial about NGRX state management. Thank you, Naveen.
ReplyDeleteFantastic. Ty.
ReplyDeleteThis is what I'm looking for, excellent tutorial. Thanks
ReplyDeleteVery impressed to see the explanation about the NGRX. KUDOS NAVEEN
ReplyDeleteVery clean and useful article! Please add a LinkedIn share button also !
ReplyDeleteGreat job but suppose I have GraphQL to connect to API do you have a tutorial about this issue
ReplyDeleteThank for this best tutorial
ReplyDelete