Introduction:
Blazor client-side framework is to build interactive client-side single page web apps which work in all modern web browsers, including mobile browser. The code is written in c# which can run on the browser like javascript frameworks (angular, react, vue etc).
In Blazor client-side framework Dotnet Code executed via WebAssembly in the browser runs in the browser's javascript sandbox securely.
Specs:
1. Asp.net core 3.0 Preview
2. Blazor (Client-side)
3. Bootstrap 4
4. VisualStudio Code Editor
Core Concept:
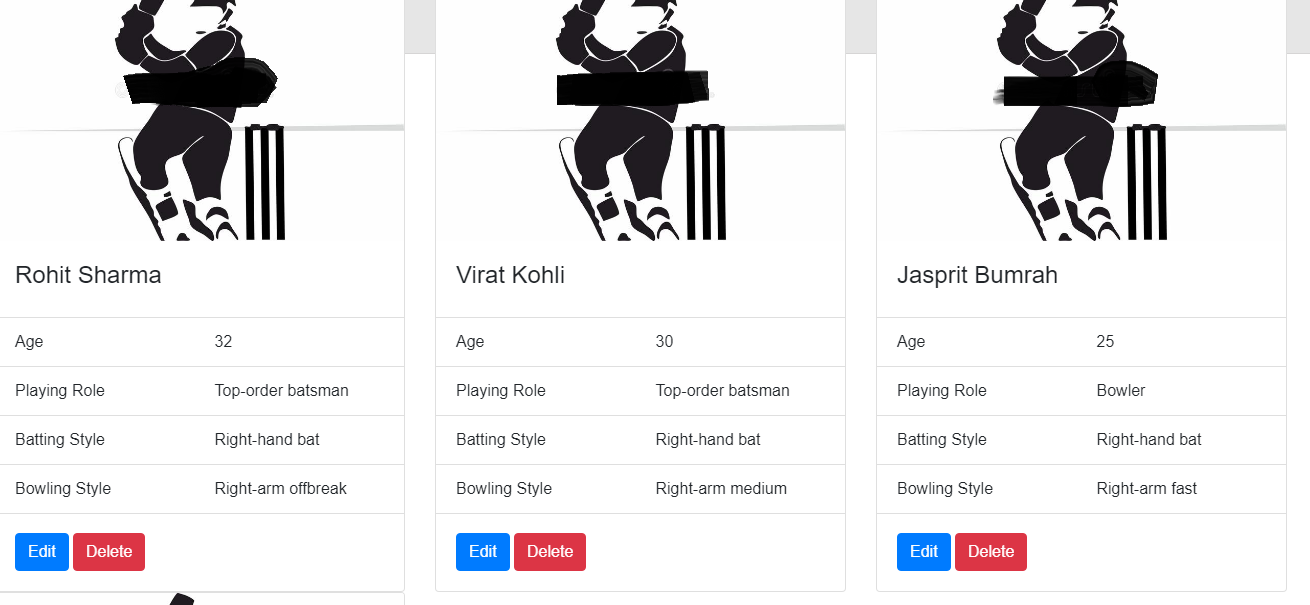
Blazor client-side application sample CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations. Let's create a sample application of the Indian cricket team players using the Blazor template. Our final sample looks as follows
Create Operation:
Step 1:
Create Blazor client-side application. Step by step process to create a blazor template.
Step 2:
Go to Pages Folder, add a new file name it as "AddPlayer.razor".Now add the following code into this razor page
Open VisualStudio code terminal and run "dotnet watch run". By default dotnet core gets to run the application with default port number 5000 then navigate to "http://localhost:5000/player/add"
Step 3:
Create a new folder name it as "Models". In the Models, folder adds a new file name it as "Player.cs" as below
In Blazor all file references need to be imported into "_import.razor" file. Now we need to import our "Player.cs" namespace as below
Step 5:
In "AddPlayer.razor" page add the Html content as follows
. "@bind" is razor syntax which helps in 2-way binding like in other javascript frameworks
. "@onclick" is razor syntax of the click event, which invokes method written c#.
Step 6:
Add the dotnet code in "AddPlayer.razor" file as follows.
. "player" instance created, which is used in Html for data 2-way binding
. "Add()" method which is bind to click event in Html
Step 7:
Now to save player records we need to call API. For that let us create a folder name it "Logics" and add that namespace in "_import.razor" file as below
Step 8:
In "Logics" folder create a file name it as "IPlayersLogic.cs" and add the following code
In the "Logics" folder create a file name it as "PlayersLogic.cs" and it will inherit the interface "IPlayerLogic.cs" file created in the above code. Add the code "PlayersLogic"
Using c# httpClient we are calling API, to create the players
Step 10:
Now to access this create an API method "PlayersLogic.cs" file into "AddPlayer.razor" file "Add()" method, we need to inject as below
Step 11:
Now after the successful creation of the player, we need to redirect to the display page (this page we will create in part 2). Blazor provided "NavigationManager" that needs to be injected in "AddPlayer.razor" as below
Step 12:
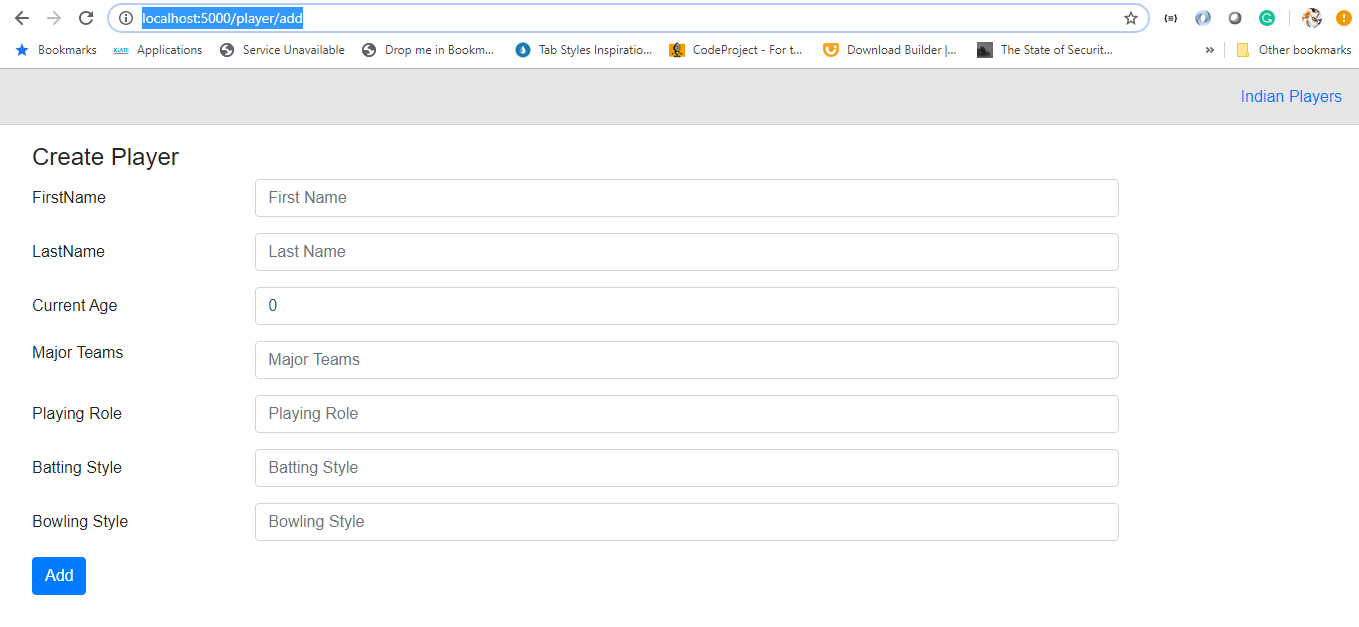
Run command "dotnet watch run" and navigate to http://localhost:5000/player/add we can see the output as below.
Refer:
. API
. Source Code
. Part-2
Specs:
1. Asp.net core 3.0 Preview
2. Blazor (Client-side)
3. Bootstrap 4
4. VisualStudio Code Editor
Core Concept:
Blazor client-side application sample CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations. Let's create a sample application of the Indian cricket team players using the Blazor template. Our final sample looks as follows
Create Operation:
Step 1:
Create Blazor client-side application. Step by step process to create a blazor template.
Step 2:
Go to Pages Folder, add a new file name it as "AddPlayer.razor".Now add the following code into this razor page
@page "/player/add"
Open VisualStudio code terminal and run "dotnet watch run". By default dotnet core gets to run the application with default port number 5000 then navigate to "http://localhost:5000/player/add"
Step 3:
Create a new folder name it as "Models". In the Models, folder adds a new file name it as "Player.cs" as below
namespace Blazor.CRUD.Sample.Models
{
public class Player
{
public int Id { get;set; }
public string FirstName { get;set; }
public string LastName { get;set; }
public int CurrentAge { get;set; }
public string Teams { get;set; }
public string PlayingRole { get;set; }
public string BattingStyle { get;set; }
public string BowlingStyle { get;set; }
}
}
Step 4:In Blazor all file references need to be imported into "_import.razor" file. Now we need to import our "Player.cs" namespace as below
@using Blazor.CRUD.Sample.Models
Step 5:
In "AddPlayer.razor" page add the Html content as follows
<h4>Create Player</h4>
<form class="justify-content-center">
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="txtFirstName" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label" >FirstName</label>
<div class="col-sm-8">
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="txtFirstName" @bind="@player.FirstName" placeholder="First Name" />
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="txtLastName" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">LastName</label>
<div class="col-sm-8">
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="txtLastName" placeholder="Last Name" @bind="@player.LastName"/>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="txtCurrentAge" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">Current Age</label>
<div class="col-sm-8">
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="txtCurrentAge" placeholder="Current age" @bind="@player.CurrentAge" />
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="txtTeams" class="col-sm-2 col-form-lable">Major Teams</label>
<div class="col-sm-8">
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="txtTeams" placeholder="Major Teams" @bind="@player.Teams" />
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="txtPlayingRole" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">Playing Role</label>
<div class="col-sm-8">
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="txtPlayingRole" placeholder="Playing Role" @bind="@player.PlayingRole" />
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="txtBattingStyle" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">Batting Style</label>
<div class="col-sm-8">
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="txtBattingStyle" placeholder="Batting Style" @bind="@player.BattingStyle" />
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="txtBowlingStyle" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">Bowling Style</label>
<div class="col-sm-8">
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="txtBowlingStyle" placeholder="Bowling Style" @bind="@player.BowlingStyle" />
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<div class="col-sm-8">
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" @onclick="Add">Add</button>
</div>
</div>
</form>
. "@bind" is razor syntax which helps in 2-way binding like in other javascript frameworks
. "@onclick" is razor syntax of the click event, which invokes method written c#.
Step 6:
Add the dotnet code in "AddPlayer.razor" file as follows.
@code
{
private Player player = new Player();
public async Task Add()
{
await _playerLogic.CreatePlayer(player);
_navigationManager.NavigateTo("players");
}
}
. "player" instance created, which is used in Html for data 2-way binding
. "Add()" method which is bind to click event in Html
Step 7:
Now to save player records we need to call API. For that let us create a folder name it "Logics" and add that namespace in "_import.razor" file as below
@using Blazor.CRUD.Sample.Logics
Step 8:
In "Logics" folder create a file name it as "IPlayersLogic.cs" and add the following code
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Blazor.CRUD.Sample.Models;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace Blazor.CRUD.Sample.Logics
{
public interface IPlayersLogic
{
Task CreatePlayer(Player player);
}
}
Step 9:In the "Logics" folder create a file name it as "PlayersLogic.cs" and it will inherit the interface "IPlayerLogic.cs" file created in the above code. Add the code "PlayersLogic"
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Blazor.CRUD.Sample.Models;
using Newtonsoft.Json;
using System.Text;
namespace Blazor.CRUD.Sample.Logics
{
public class PlayersLogic : IPlayersLogic
{
private readonly HttpClient _http;
public PlayersLogic(HttpClient http)
{
_http = http;
}
private async Task SaveOrUpdatePlayer(HttpRequestMessage request, Player player)
{
string postData = JsonConvert.SerializeObject(player);
request.Content = new StringContent(postData, Encoding.UTF8, "application/json");
HttpResponseMessage responseMessage = await _http.SendAsync(request);
return responseMessage.IsSuccessStatusCode;
}
public async Task CreatePlayer(Player player)
{
HttpRequestMessage request = new HttpRequestMessage(HttpMethod.Post, "https://localhost:44316/api/player/save");
return await SaveOrUpdatePlayer(request, player);
}
}
}
Using c# httpClient we are calling API, to create the players
Step 10:
Now to access this create an API method "PlayersLogic.cs" file into "AddPlayer.razor" file "Add()" method, we need to inject as below
@page "/player/add" @inject IPlayersLogic _playerLogic
Step 11:
Now after the successful creation of the player, we need to redirect to the display page (this page we will create in part 2). Blazor provided "NavigationManager" that needs to be injected in "AddPlayer.razor" as below
@page "/player/add" @inject IPlayersLogic _playerLogic @inject NavigationManager _navigationManager
Step 12:
Run command "dotnet watch run" and navigate to http://localhost:5000/player/add we can see the output as below.
Refer:
. API
. Source Code
. Part-2

The text in the examples is truncated. How do we get all of the code?
ReplyDeletePart 1 didn't work..... After finding the code and "filling in the blanks", it didn't work. I have 5 errors and 6 warnings and the page won't load....
ReplyDeleteMust be holes in this tutorial????
FYI.... The "localhost" number is not 5000. It's a completely different number on my computer and I believe this will be the case for each individual computer.
ReplyDeleteThis is a great posst
ReplyDelete