What Are Templated Components? :
One or more UI templates as a component parameter of type RenderFragment or RenderFragment<T>. A RenderFragment represents a chunk of UI to render.
RenderFragment Parameter:
RenderFragment parameters render the chunk of UI in a component. RenderFragment type parameter name must match with Html tag element.
Pages/Card.razor(Html Portion):
<h3>Card</h3>
<div class="card text-center">
@CardHeader
@CardBody
@CardFooter
</div>
Pages/Card.razor(@code Portion):
@code {
[Parameter]
public RenderFragment CardHeader { get; set; }
[Parameter]
public RenderFragment CardBody { get; set; }
[Parameter]
public RenderFragment CardFooter { get; set; }
}
@CardHeader, @CardBody @CardFooter are Templated Component parameters of type RenderFragment.Pages/Index.razor:
<Card>
<CardHeader>
<div class="card-header">
My Templated Component
</div>
</CardHeader>
<CardBody>
<div class="card-body">
<h5>Welcome To Template Component</h5>
</div>
</CardBody>
<CardFooter>
<div class="card-footer text-muted">
Click Here
</div>
</CardFooter>
</Card>
Each Templated Component Parameter of type RenderFragment will have a corresponding Html tag element. The Html tag element must match with the parameter name.Rendered OutPut:
Duplicate Html Tags:
The Html tag that represents the Templated component Parameter, duplicating it will result in rendering the last or bottom Html tag as a priority.Pages/Index.razor:
<Card>
<CardHeader>
<div class="card-header">
Templated Component
</div>
</CardHeader>
<CardHeader>
<div class="card-header">
Hi I'm duplicated header
</div>
</CardHeader>
</Card>
Rendered Output:
Typed RenderFragment<T> Parameter:
- RenderFragmetnt<T> a typed parameter represents to render the chunk of UI template along with some dynamic content from the type it implements.
- Declare generic type parameter at the top of the component using @typeparam. This represents the component type at runtime.
- This type of typed component parameter which passed as the element will have an implicit parameter called 'context'.
- Context implicit parameter helps in dynamic data binding. It has access to the property type that implemented by RenderFragment<T>.
Pages/Card.razor(Html Portion):
@typeparam TItem
<div class="card text-center">
@CardHeader(Item)
@CardBody(Item)
@CardFooter
</div>
Pages/Card.razor(@code Portion):
@code {
[Parameter]
public TItem Item { get; set; }
[Parameter]
public RenderFragment<TItem> CardHeader { get; set; }
[Parameter]
public RenderFragment<TItem> CardBody { get; set; }
[Parameter]
public RenderFragment CardFooter { get; set; }
}
CardHeader, CardBody are component parameters of type RenderFragment<T>. These properties templated Html have access to implicit parameter 'context' for dynamic binding data.Pages/Index.razor(Html Portion):
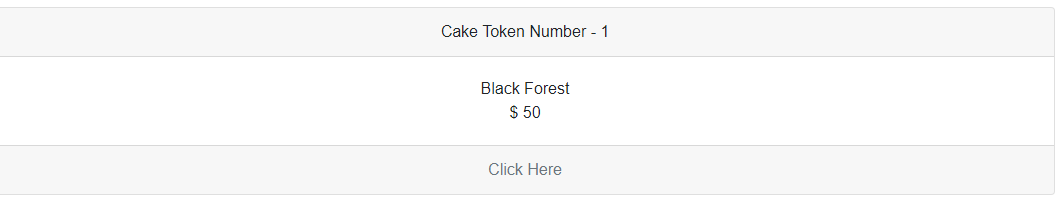
<Card Item="Cake">
<CardHeader>
<div class="card-header">
Cake Token Number - @context.Id
</div>
</CardHeader>
<CardBody>
<div class="card-body">
<div>@context.Name</div>
<div>$ @context.Cost</div>
</div>
</CardBody>
<CardFooter>
<div class="card-footer text-muted">
Click Here
</div>
</CardFooter>
</Card>
Dynamic data binding inside the templated Html elements using implicit parameter 'context'.Pages/Index.razor(@code Portion):
@code{
private Cake Cake = new Cake
{
Id = 1,
Name = "Black Forest",
Cost = 50
};
}
Models/Cake.cs:
public class Cake
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public decimal Cost { get; set; }
}
Rendered Output:
Context Attribute On Templated Html Element:
In the templated Html element, context can be declared explicitly as the Html attribute. The value assigned to the Context (Html attribute) will be used for dynamic binding in the templated Html element.
Declaring Context attribute at the Component Html element level.
Pages/Index.razor:
<Card Item="Cake" Context="cakeContext">
<CardHeader>
<div class="card-header">
Cake Token Number - @cakeContext.Id
</div>
</CardHeader>
<CardBody>
<div class="card-body">
<div>@cakeContext.Name</div>
<div>$ @cakeContext.Cost</div>
</div>
</CardBody>
</Card>
Declaring Context attribute at the each templated Html level.
Pages/Index.razor:
<Card Item="Cake">
<CardHeader Context="headContext">
<div class="card-header">
Cake Token Number - @headContext.Id
</div>
</CardHeader>
<CardBody Context="bodyContext">
<div class="card-body">
<div>@bodyContext.Name</div>
<div>$ @bodyContext.Cost</div>
</div>
</CardBody>
</Card>
'headContext', 'bodyContext' are context parameters of templated Html.Generic-typed Templated Component:
Templated component itself a generic typed component. @typeparam to define the type of the generic component. Generic-typed templated component will be defined by our own implementation of it and how it can be reused for different types.
The best choice of its implementation Generic-typed component is like the component with only two properties. The first property is of type RenderFragment<T> templated property to render the Html. The Second property is of type List<T> a collection of data to be bind to the rendered Html.
The most widely used scenarios for the Generic-typed templated component is of display items, it will help to avoid to create new components for displaying items in an application. Single component for all display items.
Pages/ShowItems.razor(Html portion):
@typeparam TItem
<div>
@if ((Items?.Count ?? 0) != 0)
{
@foreach (var item in Items)
{
@ShowTemplate(item);
}
}
</div>
Pages/ShowItems.razor(@code portion):
@code {
[Parameter]
public RenderFragment<TItem> ShowTemplate { get; set; }
[Parameter]
public List<TItem> Items { get; set; }
}
ShowTemplate and Items are two parameters of our generic-typed component. ShowTemplate is of type RenderFragment property which will render Html to display (this Html can be table, list, content, etc,). Items are collection property whose type is matches with our component type, this data will be used in the data binding inside of our rendered Html.Pages/Index.razor(Html portion):
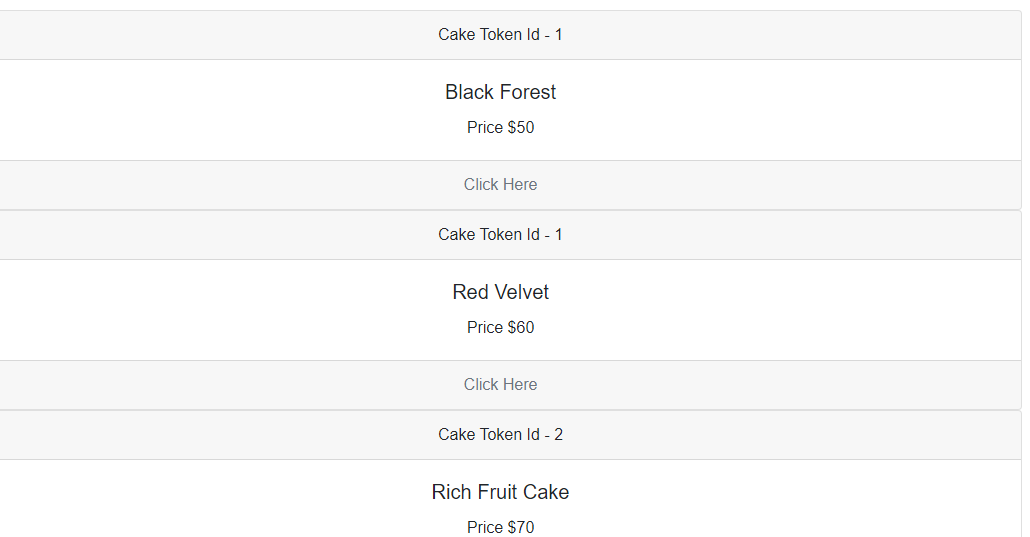
<ShowItems Items="Cakes" >
<ShowTemplate Context="CakeContext">
<div class="card text-center">
<div class="card-header">
Cake Token Id - @CakeContext.Id
</div>
<div class="card-body">
<h5 class="card-title">@CakeContext.Name</h5>
<p class="card-text">Price $@CakeContext.Cost</p>
</div>
<div class="card-footer text-muted">
Click Here
</div>
</div>
</ShowTemplate>
</ShowItems>
ShowItems template represents our generic-typed component. ShowTemplate represents component Html rendering property.Pages/Index.razor(@code portion):
@code{
public List<Cake> Cakes { get; set; }
protected override Task OnAfterRenderAsync(bool firstRender)
{
LoadCakes();
StateHasChanged();
return base.OnAfterRenderAsync(firstRender);
}
public void LoadCakes()
{
Cakes = new List<Cake>
{
// items hidden for display purpose
new Cake
{
Id = 1,
Name = "Red Velvet",
Cost = 60
},
};
}
}
Inside life cycle method 'OnAfterRenderAsync' method, calling 'StageHasChanged()' method to reflect the data changes in component. You can try removing the 'StateHasChanged()' method where we can observe an empty page without displaying data because we are populating data ofter rendering Html.Rendered Output:
Using HttpClient:
In Blazor application, data will be consumed by calling Web API using 'System.Net.Http.IHttpClientFactory'.
To serialize or deserialize the JSON data from an API using NewtonSoft.Json Nuget.
Install-Package Newtonsoft.Json -Version 12.0.3
IHttpClientFactory can be used by injecting from the constructor. To inject it need to register HttpClient services in the Startup.cs
Startup.cs:
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
// hiden code for display purpose
services.AddHttpClient();
}
Add Logic file to fetch the data from an API
Logic/CakeLogic.cs:
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Blazor.TemplateComponent.App.Models;
using Newtonsoft.Json;
namespace Blazor.TemplateComponent.App.Logic
{
public class CakeLogic : ICakeLogic
{
private readonly IHttpClientFactory _httpClientFactory;
public CakeLogic(IHttpClientFactory httpClientFactory)
{
_httpClientFactory = httpClientFactory;
}
public async Task<IList<Cake>> GetAll()
{
HttpRequestMessage request = new HttpRequestMessage(HttpMethod.Get, "https://localhost:44316/api/cake/get");
var httpClient = _httpClientFactory.CreateClient();
HttpResponseMessage responseMessage = await httpClient.SendAsync(request);
if (responseMessage.IsSuccessStatusCode)
{
string data = await responseMessage.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(data))
{
return JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<List<Cake>>(data);
}
}
return null;
}
}
}
Logic/ICakeLogic.cs:
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Blazor.TemplateComponent.App.Models;
namespace Blazor.TemplateComponent.App.Logic
{
public interface ICakeLogic
{
Task<IList<Cake>> GetAll();
}
}
Now register the logic files in a startup.cs file so that the logic files can be injected anywhere in the application.
Startup.cs:
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
// hidden code for display purpose
services.AddSingleton<ICakeLogic, CakeLogic>();
services.AddHttpClient();
}
Add required namespaces globally in _Import.razor.
_Import.razor:
@using Blazor.TemplateComponent.App.Models @using Blazor.TemplateComponent.App.Logic
Now update the Index. razor file to consume the data from the API.
Index.razor(@Html Portion):
@inject ICakeLogic _cakeLogic
Index.razor(@code Portion):
@code{
public List<Cake> Cakes { get; set; }
protected override async Task OnAfterRenderAsync(bool firstRender)
{
await LoadCakes();
StateHasChanged();
await base.OnAfterRenderAsync(firstRender);
}
public async Task LoadCakes()
{
var result = await _cakeLogic.GetAll();
Cakes = result.ToList();
}
}
Render Output:
Wrapping Up:
Hopefully, this article will help you with an understanding of Blazor Templated Component and Generic-Typed Templated Component. I will love to have your feedback, suggestions, and better techniques in the comments section.




Comments
Post a Comment