Introduction:
A Page or Form or Dialog is used to construct a Blazor Application are made of Components. A Component is a block of code consist of C# + HTML + CSS. Components give the advantage of code splitting, nesting, and reusability.
In this journey, we are going to explore Blazor components with sample examples.
Blazor Or Razor Component:
Blazor components can be called Razor Components because they implemented in a Razor file(.razor). In general, the component is a combination of C# @code block and Html UI of Razor syntax.
A simple component with c# code and Html as below:
Pages/Parent.razor:
<h3>Hey I'm Parent Component</h3>
@code {
}
Component Naming Convention:
Blazor Components should always start with a capital letter. Trying to create a component name with a small casing letter leads to a compilation error.
Example create a component as 'Pages/parent.razor' result error as below
@code block:
C# @code block is like a class where we can declare properties and methods. It also contains Life-Cycle methods of the component in addition to the user-defined logical serving methods.
@code {
public string Heading => "Hey I'm Parent Component";
public void DoSomething()
{
// method serves user logic
}
protected override Task OnInitializedAsync()
{
// Blazor component life-cycle method
return base.OnInitializedAsync();
}
}
Multiple @code block:
Yes, it possible to use multiple @code blocks. It doesn't mean we can create duplicate methods or properties with the same names in different @code blocks, such implementation will give compilation errors. Because of razor file compiled to a partial class where classes won't allow parameters or methods with the same name.
Pages/Parent.razor(Html Portion):
<h3>@FirstBlock</h3> <h3>@SecondBlock</h3>
Pages/Parent.razor(@code Portion):
@code {
public string FirstBlock => "Hey I'm from fisrt @Code Block";
}
@code
{
public string SecondBlock => "Hey I'm from second @code Block";
}
Rendered Output:
Code Behind File OR Partial Razor Class:
In Microsoft Web Technologies a beautiful feature to separate Html and C# code by using the code-behind file. Blazor components also support to use code-behind files. The code-behind file class must be a partial class. The Reason behind the partial class is the razor file on the compilation converted as a partial class. The code-behind file name extension "{componentName}.razor.cs".
Pages/Parent.razor:
<h3>@Heading</h3>Pages/Parent.razor.cs(code-behind file):
public partial class Parent
{
public string Heading => "Hey I'm from component's code behind file Parent.razor.cs";
}
Rendered Output:Component Html Tag:
Component Html Tag is a custom Html tag whose name must match with the component file name. By default Html, Tag needs to be used with a fully qualified name for example like
{ProjectName}.Pages.{componentName} , {ProjectName}.Pages.{FolderName}.{componentName}, etc.
Pages/Index.razor:
<Blazor.Component.Test.App.Pages.Sample1.Parent></Blazor.Component.Test.App.Pages.Sample1.Parent>
Tag Name can be shortened by importing the namespace into the _Import.razor file
_Import.razor:
@using Blazor.Component.Test.App.Pages.Sample1;Pages/Index.razor:
<Parent></Parent>
[Parameter] Attribute Or Component Parameter:
A property of component decorated with [Parameter] attribute can be called as Component Parameter. Component Parameter has the ability to take input from the HTML attribute (whose name must match the Component Parameter variable name) of component markup tag. Component Parameter access specifier should always be 'public' so that property will available for component markup tag.
Pages/Parent.razor(Html Portion):
<h3>@Heading</h3>Pages/Parent.razor(@code Portion):
@code {
[Parameter]
public string Heading { get; set; }
}
Pages/Index.razor:
<Parent Heading="Hello I'm from Parent tag markup"> </Parent>Rendered Output:
Component Data Binding OR 2-way Data Binding:
In Blazor components it is possible to do 2-way binding using '@bind' attribute which takes a c# property as its input.
Pages/Parent.razor(Html Portion):
<h3>@Heading</h3> <input type="text" @bind="Heading"/>
Pages/Parent.razor(@code Portion):
@code {
public string Heading { get; set; }
}
Rendered Output:
UI Events:
Like any other front-end frameworks, Blazor also supports UI Events like click, change, focus, etc. In a component, we can register events with methods in the component. Example to register click event like @onclick="methodName".
Pages/Parent.razor(Html Portion):
Pages/Parent.razor(Html Portion):
<h3>Click button to increase My Rank @Count</h3> <button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" @onclick="Increment">Click Me</button>Pages/Parent.razor(@code Portion):
@code {
public int Count { get; set; }
private void Increment()
{
Count = Count+1;
}
}
Rendered Output:@ref To Access Component:
- Using @ref can access the child component, public members.
- @ref expects a property from the parent component and that property of type is child component type.
- After components rendered the instance of child component will be assigned to the property(in the parent component) of the type child component.
- Using this reference parameter we can access members of child component and modify them, but to reflect the changes we need to call "base.stateHasChanged()" in the child component.
<h3>Parent</h3> <button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" @onclick="PassDataToChild">Click Me</button> <Child @ref="child"></Child>Pages/Parent.razor(@code Protion):
@code {
private Child child;
private void PassDataToChild()
{
child.UpdateHeading("Hi on parent button clicked my child heading changes");
}
}
Pages/Child.razor(Html Portion):
<h3>@Heading</h3>Pages/Child.razor(@code Portion):
@code {
public string Heading { get; set; }
public void UpdateHeading(string heading)
{
Heading = heading;
base.StateHasChanged();
}
}
Rendered Output:Conditional Display Components:
Yes it possible to hide and show a component using razor sytax of "@if".
Pages/Parent.razor(Html Portion):
<h3>Parent</h3>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" @onclick="ToggleChildComponent">Click Me Toggle Child Component</button>
@if (showChild)
{
<Child ></Child>
}
Pages/Parent.razor(@code Portion):
@code {
bool showChild = true;
private void ToggleChildComponent()
{
showChild = !showChild;
}
}
Pages/Child.razor:
<h3>I'm child Component</h3>
@code {
}
Rendered Output:Looping Components:
Yes, it is possible to loop a component using razor "@for". On every iteration, the new component will be rendered, which are independent of components rendered in the previous iteration or next iteration.
Pages/Parent.razor:
<h3>Parent</h3>
@for (int i=0;i < 3;i++)
{
<Child ></Child>
}
@code {
}
Pages/Child.razor:
<h3>I'm child Component</h3>
@code {
}
Rendered Output:Wrapping Up:
Hopefully, this article gives you a basic understanding of blazor components. I will love to have your feedback, suggestions, and better techniques.






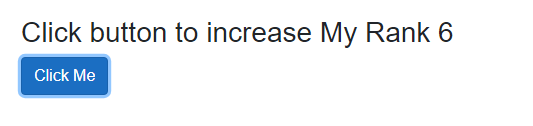



Comments
Post a Comment