What Is GraphQL?:
GraphQL is a query language for your API and a server-side runtime for executing queries by using a schema type system you defined for your data. Graphql is not tied to any specific programming language(like NestJS, Java, .NET, etc) or database or storage engine.
How GraphQL Different From Rest API:
- GraphQL exposes a single endpoint.
- HTTP-POST is the only Http verb recommended by GraphQL.
- Client applications(consumers of GraphQL API) can give instructions to GraphQL API about the response data.
Schema vs Code First Approach:
Schema First Approach - GraphQL SDL (Schema definition language) is a new syntax language, which is independent of any programming language and also integrates with any programming language. But while integrating with any programming language GraphQL Schema needs to be mapped with objects or classes or interface of the specific programming language to build communication between GraphQL Schema and programming language. In NestJS this communication channel will be built automatically by generating files in the form Typescript Classes or Interfaces based on the GraphQL schema define by you.
Code First Approach - In this approach TypeScript Classes and its fields use decorators on them which will generate corresponding GraphQL Schema automatically. Here we don't specify GraphQL SDL explicitly which helps developers to have less concentration on GraphQL Schema syntax.
Create NestJS Application:
Here we going to create a sample NestJS application with GraphQL integration using Schema first Approach.
NestJS Installation Command: npm i -g @nestjs/cli
NestJS Application Creation Command: nest new your-project-name
GraphQL NPM Packages:
Now run the following commands to install GraphQL packages required for our application.
1. npm i --save @nestjs/graphql
2. npm i --save graphql-tools
3. npm i --save graphql
Define GraphQL Schema:
GraphQL Schema is constructed by object types, most object types represent the domain object(domain object means a class or interface in an application that represents a table in the database). Query and Mutation are default object types of GraphQL Schema, these object types represent the operations like fetching or updating an API.
Now let's define GraphQL Schema object type that represents our application domain object as below.
src/student/student.grahpql(file extension *.grahql):
type Student{
_id: String,
FirstName: String,
LastName: String,
Standard: Int,
FatherName: String,
MotherName: String
}
- The schema object type almost looks like a JSON object.
- The Schema object begins with 'type' keyword and 'Student' is the name we defined for the Schema object type.
- The Schema has a set of properties these must match with our domain object(class or interface in typescript represents a table in the database).
- GraphQL Schema has a set of pre-defined data types like 'Int', 'String', etc which looks similar to most of the programming language types.
Define GraphQL Schema Query Object Type:
The 'Query' object type is a default type in GraphQL Schema. 'Query' constructs all definitions to filter definitions of our API(simple words it contains all method definitions to filter and fetch data).
Let's define filter definitions for our 'Student' object type as below.
src/student/student.graphql(file extension *.graphql):
type Query{
getAllStudents:[Student],
getStudentById(id:String):Student
}
- GraphQL Schema Query object holds all the definitions for filtering API.
- 'getAllStudents()' definition to fetch all data and [Student](name should match with our GraphQL Schema object type we defined in an earlier step) represents an array of 'Student' object types.
- 'getStudentById(id:string)' definition to fetch single object type with matched input value 'id'.
Import GraphQLModule:
In AppModule of our application, we need to register the GraphQLModule as below.
src/app.module.ts:
import { GraphQLModule } from '@nestjs/graphql';
import { join } from 'path';
@Module({
imports: [
GraphQLModule.forRoot({
typePaths: ['./**/*.graphql'],
definitions:{
path: join(process.cwd(),'src/graphql.schema.ts')
}
})
]
})
export class AppModule {}
// code hidden for display purpose
- Inside import array registered 'GraphQLModule.forRoot({})' from '@nestjs/grahpql' library.
- 'GraphQLModule.forRoot({})' the module takes input configuration object with properties like 'typePaths', 'definitions'.
- 'typPaths' used to access all GraphQL Schema defined files and it takes collection of file paths as input.
- './**/*.graphql' defines folder paths to search for graphql files, './'(mostly represents 'src') root path, '/**/' defines all folder and it subfolders, '*.graphql' all files inside the folders with '.graphl' file extension.
- 'definitions' takes an object which contains property like 'path', the use of this 'path' property to auto generate the typescript classes or interface based on the GraphQL object types. So for this 'path' property need specify location for '*.ts'(like 'src/grahql.schema.ts') generation.
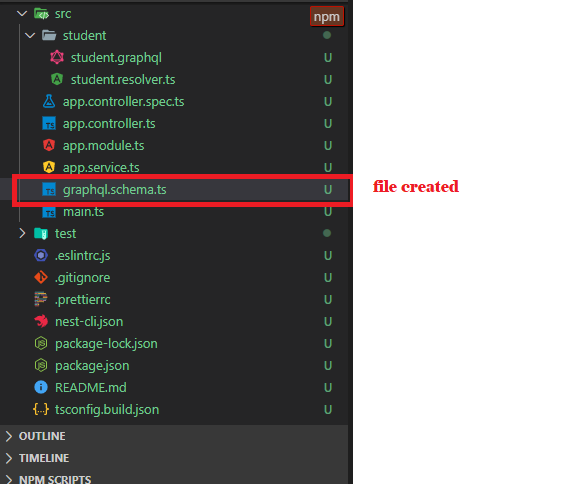
Auto-Generated GraphQL Schema To Typescript Classes or Interfaces:
On application start, all the GraphQL Schema objects are collected and generates matching typescript classes or interface for build communication between typescript and GraphQL schema.
To check application start commands go to package.json file and check the scripts object inside it.
Development command to start the application: npm run start:devOn application started, the schema file gets crated as below.
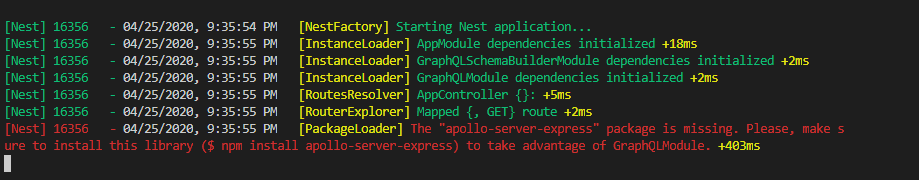
On starting the application if the build fails as below
Then install the required package shown in the error above.
npm install apollo-server-express
Service Provider:
In general service provider contains logic to fetch the data from databases. Let's create a service provider with test data as follows.
src/student/student.service.ts:
import {Student} from '../graphql.schema';
export class StudentService {
students:Student[]=[{
_id:"abc1",
FirstName: "Naveen",
LastName: "Bommidi",
Standard: 7,
FatherName: "Gopala Krishna",
MotherName: "Mallikasulamma"
}]; // while testing graphql api add more test data
getAllStudents():Student[]{
return this.students;
}
getStudentById(id:string):Student{
var filteredStudent = this.students.filter(_ => _._id === id)[0];
return filteredStudent;
}
}
'Student' type importing from auto-generated classes or interface based on the schema object type.Now import service provider in app.module.ts file as follows.
app.module.ts:
import {StudentService} from './student/student.service';
@Module({
providers: [StudentService],
})
export class AppModule {}
// code hidden for display purpose
Resolver:
Resolver is used to implement the GraphQL operation like fetching or saving data, based on default schema object types like 'Query'(contains definition for filtering and fetching data) or 'Mutation'(contains definition for creating or updating data).
Let's resolve the 'Query' object type in 'student.graphql' file as below.
src/student/student.resolver.ts:
Let's resolve the 'Query' object type in 'student.graphql' file as below.
src/student/student.resolver.ts:
import { Resolver, Query, Args } from '@nestjs/graphql';
import { StudentService } from './student.service';
import { Student } from '../graphql.schema';
@Resolver('Student')
export class StudentResolver {
constructor(private studentService: StudentService) {}
@Query()
getAllStudents(): Student[] {
return this.studentService.getAllStudents();
}
@Query()
getStudentById(@Args('id') id: string):Student{
return this.studentService.getStudentById(id);
}
}
- '@Resolver()' imported from '@nestjs/graphql' package, it should be decorated over the class to make it resolver class and it takes optional string input parameter where we pass the name of the GraphQL schema object type(eg: Student).
- '@Query()' imported from '@nestjs/graphql', this decorator represents the 'Query' object type in GraphQL Schema and it should be decorated over the implemented methods of the 'Query' object type
- '@Arg()' is capture the input values from the clients.
import { StudentResolver } from './student/student.resolver';
@Module({
providers: [StudentResolver],
})
export class AppModule {}
// hidden some code for display purpose
GraphQL UI Playground:
GraphQL UI Playground is the page which helps as a tool to query our GraphQL API (if we compare with REST API UI Playground is like Swagger). This Playground gives Schema information, GraphQL Documentation, Intelligence to type the queries more quickly. GraphQL constructed only one endpoint and supports only Http Post verb, so to access this UI Playground simply use same endpoint in the browser directly.
Fields:
GraphQL is about asking for specific fields on objects on the server. Only requested fields will be served by the server.
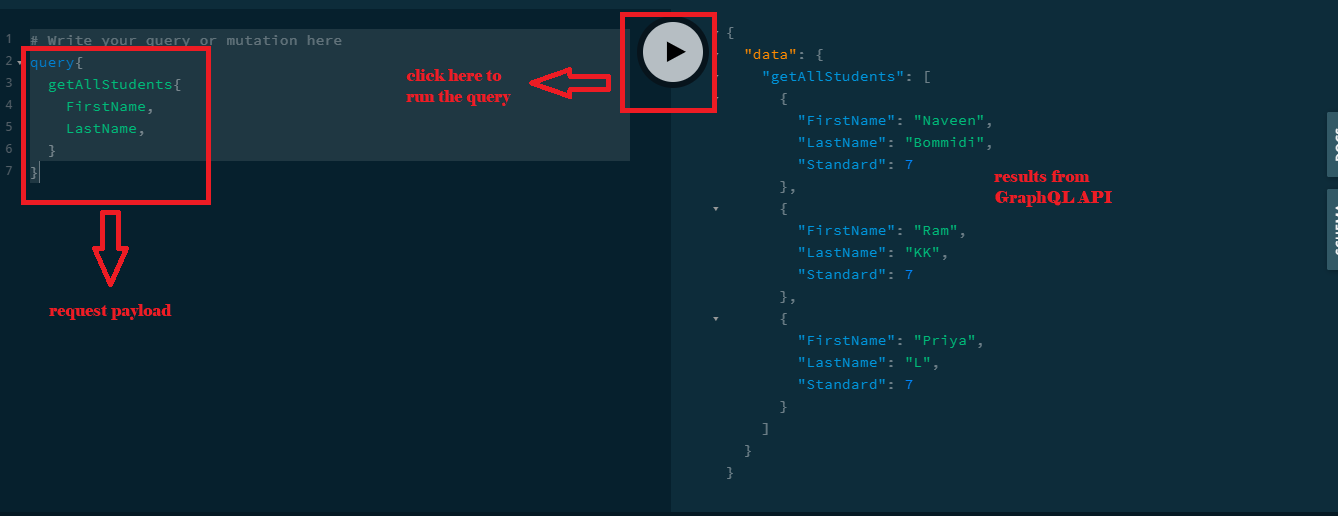
Let's query a few fields from the 'Student' schema as follow.
query{
getAllStudents{
FirstName,
LastName,
}
}
- 'query' keyword to identify the request is for fetching or querying data based on 'Query' Schema object at the server.
- 'getAllStudents' keyword to identify the definition or method inside of the 'Query' schema object.
- 'FirstName', 'LastName' are fields inside of the 'Student' GraphQL object type we created.
Input Arguments To Filter Data:
In GraphQL we can pass arguments to filter the Data. Let's construct the query as below with a filtering argument.
query{
getStudentById(id:"abc2"){
FirstName,
LastName,
Standard
}
}
In 'Query' object type we have a definition 'getStudentById' which takes an input parameter, the above query is to execute this definition.Aliases:
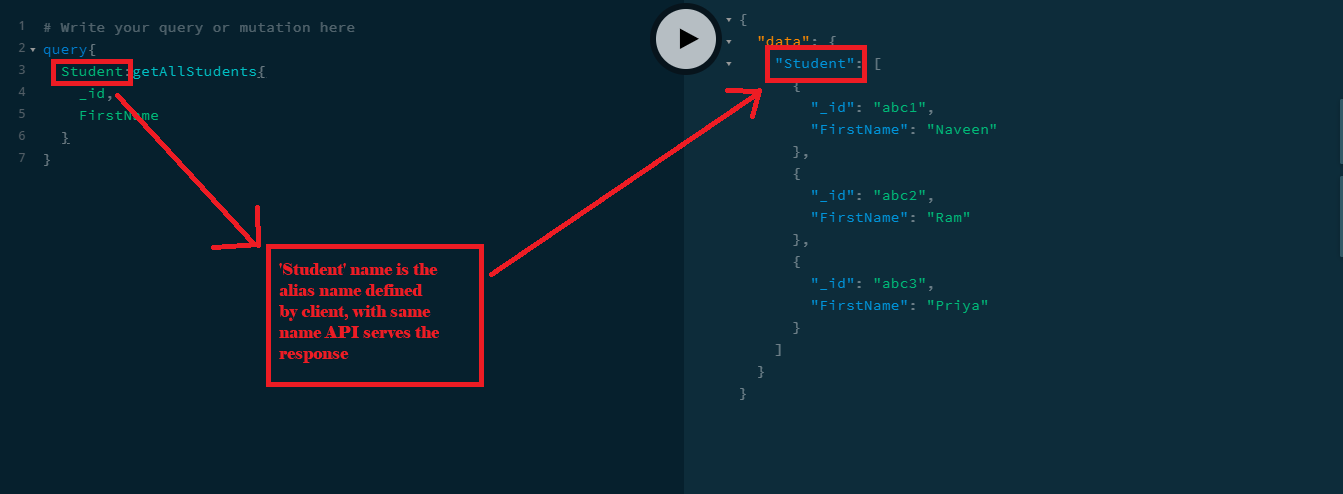
While querying the GraphQL API with schema definition names like 'getAllStudents', 'getStudentById' are more self-explanatory, which good for requesting the API. But API on returning a response uses the same definition name as main object name which looks bit different naming convention for JSON response object. In GraphQL to overcome this scenario, we can use 'Aliases' names which are defined by the client, the API will serve the response with those names.
query{
Student:getAllStudents{
_id,
FirstName
}
}
Here 'Student' is the alias name for 'getAllStudents'.Fragments:
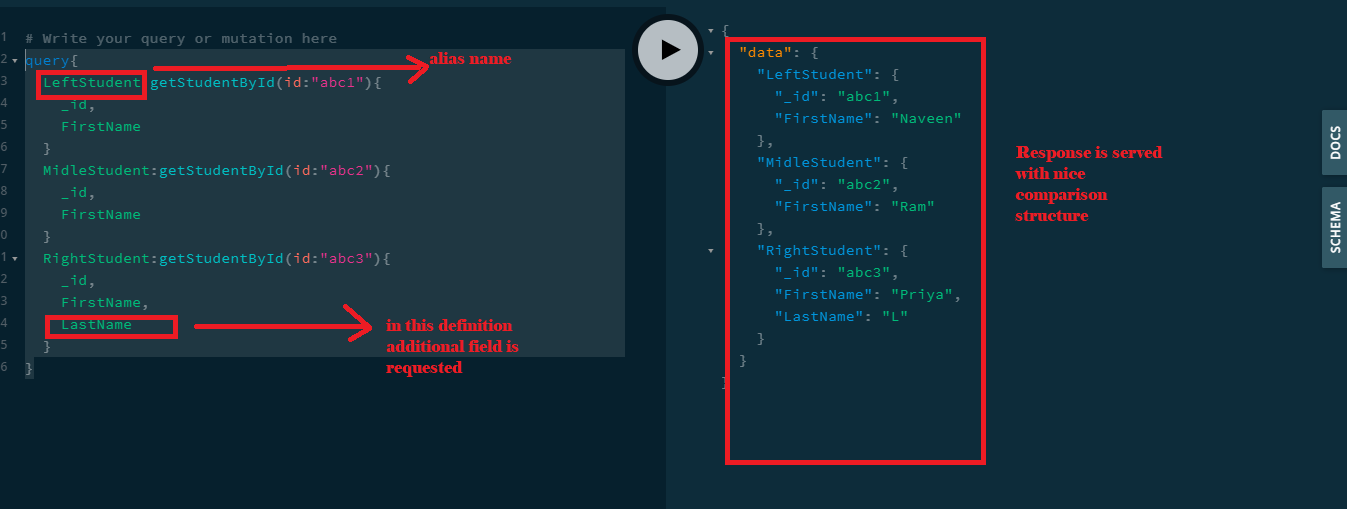
Fragments in GraphQL API mean comparison between two or more records. A comparison between 2 or more items is very easy in GraphQL.
query{
LeftStudent:getStudentById(id:"abc1"){
_id,
FirstName
}
MidleStudent:getStudentById(id:"abc2"){
_id,
FirstName
}
RightStudent:getStudentById(id:"abc3"){
_id,
FirstName,
LastName
}
}
Defining a schema definition payload multiple times inside of the query object is called Fragments. The fragment is only possible between the same type of schema definition if you try to execute between different schemas that lead to error. In each definition you can define any number of field names, it is not mandatory to define the same number field names in all definitions as in the above query.Mutation:
GraphQL Mutation object type deals with data updates. All the definitions in the Mutation object type have the responsibility of saving or updating the data to storage (like a database).
For saving data in the Mutation object type definition we need to pass an argument that should be an object. In GraphQL Schema to create an argument object, we need to construct an object type as follows.
src/student/student.graphql:
input StudentInput{
_id:String
FirstName: String,
LastName: String,
Standard: Int,
FatherName: String,
MotherName: String
}
Object type constructed with 'input' keyword is used for argument variable type for the definitions either in 'Query' or 'Mutation' object types.Let's define the Schema definition in Mutation object type as follows
src/student/student.graphql:
type Mutation{
create(student:StudentInput):Student
}
'StudentInput' is used to input argument for creating definitions.
Note: You can't use 'Student' object type as an argument type in 'create' definition, because in graphql object get created by using 'input' keyword to use as an argument type.Let's update the service provider class as follows.
src/student/student.service.ts:
import {Student} from '../graphql.schema';
export class StudentService {
// code hidden for display purpose
createStudent(newStudent:any):Student{
this.students.push(newStudent);
return newStudent;
}
}
Let's now update the resolver class by implementing the 'create' definition in the Mutation object type as follows.
src/student/student.resolver.ts:
import {Args, Mutation } from '@nestjs/graphql';
import { StudentService } from './student.service';
import { Student, StudentInput } from '../graphql.schema';
@Resolver('Student')
export class StudentResolver {
constructor(private studentService: StudentService) {}
@Mutation()
create(@Args('student')student:StudentInput):Student{
return this.studentService.createStudent(student);
}
}
In resolve class, while implementing the definition in 'Mutation' object type then we need to use '@Mutation()' decorator on top of the implemented method. 'StudentInput' class which auto-generated from GraphQL Schema to 'src/graphql-schema.ts' file.Now to create GraphQL query to save a new item as follows
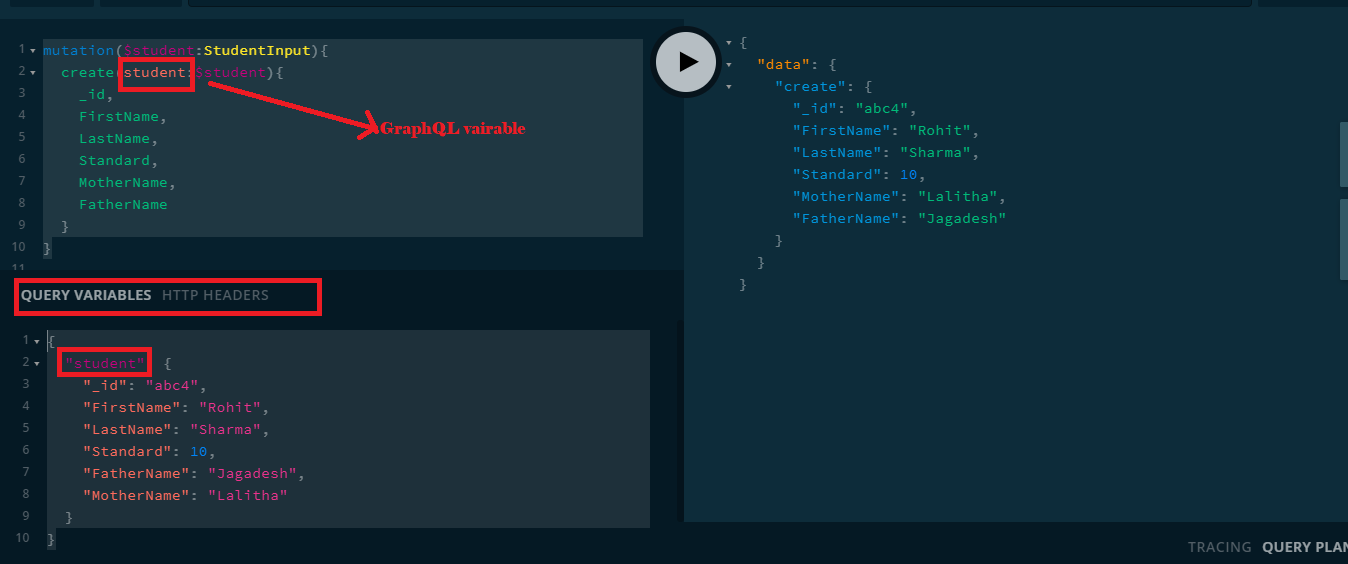
Mutation:
mutation($student:StudentInput){
create(student:$student){
_id,
FirstName,
LastName,
Standard,
MotherName,
FatherName
}
}
Variable:
{
"student": {
"_id": "abc4",
"FirstName": "Rohit",
"LastName": "Sharma",
"Standard": 10,
"FatherName": "Jagadesh",
"MotherName": "Lalitha"
}
}
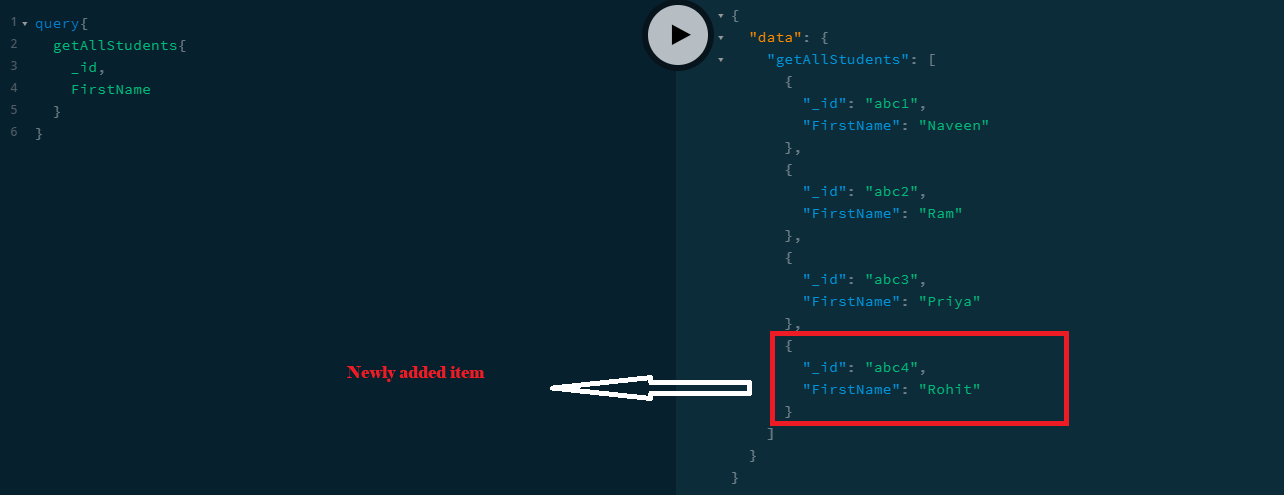
This is a way to send data to save in graphql, "student" in JSON object must match with the name with an input parameter of 'create()' method which means 'student' is GraphQL variable.Test the new item added by using a query as follow.
Wrapping Up:
Hopefully, this article will help to understand the GraphQL API integration in the NestJS application using Schema First Approach. I love to have your feedback, suggestions, and better techniques in the comment section.





Really helpful start for me ! Thanks
ReplyDeleteWhy is id prefixed with underscore (_id)?
ReplyDelete