Part-1 Hot Chocolate GraphQL JWT(JSON Web Token) Authentication - Generating User Login Access Token
In this article, we are going to implement a JWT authentication sample for the Hot Chocolate GraphQL endpoint.
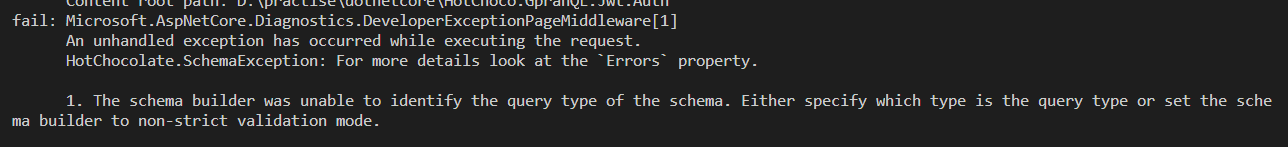
The above image displaying an error, this error occurs when we try to access the GraphQL endpoint. So from the error, we have to understand that our GraphQL endpoint expecting a Query object. But till now we don't have the necessity to create a Query object. So to fix the issue we will create a Query object with one dummy resolver method.
It's purely optional to implement JWT authentication in the GarphQL approach. Because .Net supports endpoint configuration for both normal .Net endpoint and GraphQL endpoint. While implementing GraphQL in your application and if you want to develop an authentication endpoint in the .Net approach there is no issue. But if you want to develop all endpoint in GraphQL including authentication that is also fine. So in this article, our goal is to create JWT authentication as a GraphQL endpoint.
Create A .Net5 Web API Application:
To understand the concept let's start our journey by creating a sample .Net5 Web API application.
Recommended IDE for development are like Visual Studio 2019(Version 16.8.* for .Net5) or Visual Studio Code.
Install Hot Chocolate Library:
Package Manager Command:
Install-Package HotChocolate.AspNetCore -Version 11.0.2.Net CLI Command:
dotnet add package HotChocolate.AspNetCore -Version 11.0.2
Configure GraphQL Service And EndPoint:
First, we need to configure the GraphQL service and GraphQL endpoint as a beginning step.
Startup.cs:(ConfigureServices Method)
services.AddGraphQLServer();Startup.cs:(Configure Method):
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapGraphQL();
endpoints.MapControllers();
});
Use Either Query Type Or Mutation Type:
In GraphQL it is recommended to Http Post verb for invoking endpoint. In GraphQL for posting user credentials either we can use Query or Mutation type. But my recommendation is to use the Mutation Type because on authenticating user we might have to update some data in table like UserLastLogin, RefreshToken, etc.
Create User Payload C# Model And GraphQL InputObjectType:
Now we have to create payload model that contains information about 'Email' and 'Password'.
Models/LoginInput.cs:
namespace HotChoco.GprahQL.Jwt.Auth.Models
{
public class LoginInput
{
public string Email { get; set; }
public string Password { get; set; }
}
}
Now we need to create GraphQL InputObjectType that will understand the c# Model 'LoginInput'.GraphQLModel/InputModel/LoginInputObjectType.cs:
using HotChoco.GprahQL.Jwt.Auth.Models;
using HotChocolate.Types;
namespace HotChoco.GprahQL.Jwt.Auth.GraphQLModel.InputModel
{
public class LoginInputObjectType: InputObjectType<LoginInput>
{
protected override void Configure(IInputObjectTypeDescriptor<LoginInput> descriptor)
{
descriptor.Field(_ => _.Email).Type<StringType>().Name("Email");
descriptor.Field(_ => _.Password).Type<StringType>().Name("Password");
}
}
}
- LoginInputObject is GraphQL understandable of model that is equivalent to the 'LoginInput' c# model. That is possible by inheriting the 'InputObjectType<LoginInput>'. All properties of 'LoginInput' need to be registered as 'Field' in 'LoginInputObjectType'.
Add User.cs File:
Create User.cs file which will represent 'Users' table.
Data/Entities/User.cs:
Data/Entities/User.cs:
namespace HotChoco.GprahQL.Jwt.Auth.Data.Entities
{
public class User
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public string Email { get; set; }
public string Password { get; set; }
public string PhoneNumber { get; set; }
}
}
Create User Login Mutation Resolver Method:
Now we have to create login user mutation method in our sample application. For now we are going use mock user data to test the user exist or not.
So let's add the mock user data.
GraphQLCore/Mutation.cs:
private List<User> Users = new List<User>
{
new User{
Id = 1,
FirstName = "Naveen",
LastName = "Bommidi",
Email = "naveen@gmail.com",
Password="1234",
PhoneNumber="8888899999"
},
new User{
Id = 2,
FirstName = "Hemanth",
LastName = "Kumar",
Email = "hemanth@gmail.com",
Password = "abcd",
PhoneNumber = "2222299999"
}
};
Now let's implement the skeleton for our user login resolver method as below.GraphQLCore/Mutation.cs:
public string UserLogin(LoginInput login)
{
var currentUser = Users.Where(u => u.Email.ToLower() == login.Email &&
u.Password == login.Password).FirstOrDefault();
if (currentUser != null)
{
return "for now i'm dummy jwt access token";
}
return string.Empty;
}
- In this resolver, for now, we check the user payload against our mock user data if the user found then returning some fakes string as an access token.
GraphQLModel/ObjectType:
using HotChoco.GprahQL.Jwt.Auth.GraphQLCore;
using HotChoco.GprahQL.Jwt.Auth.GraphQLModel.InputModel;
using HotChocolate.Types;
namespace HotChoco.GprahQL.Jwt.Auth.GraphQLModel.ObjectType
{
public class MutationObjectType: HotChocolate.Types.ObjectType<Mutation>
{
protected override void Configure(IObjectTypeDescriptor<Mutation> descriptor)
{
descriptor.Field(_ => _.UserLogin(default))
.Type<StringType>()
.Name("UserLogin")
.Argument("login", a => a.Type<LoginInputObjectType>());
}
}
}
- Here we registered our resolver method as 'Field'.
- The 'Name' extension method to specify the name of the field. This same name will be used to calling mutation from the client application.
- The 'Argument' extension method to map the user payload to our resolver method. Here if you observe that the argument type declared as 'LoginInputObjectType' which understandable by GraphQL on execution internally it will map with our c# class called 'LoginInput'.
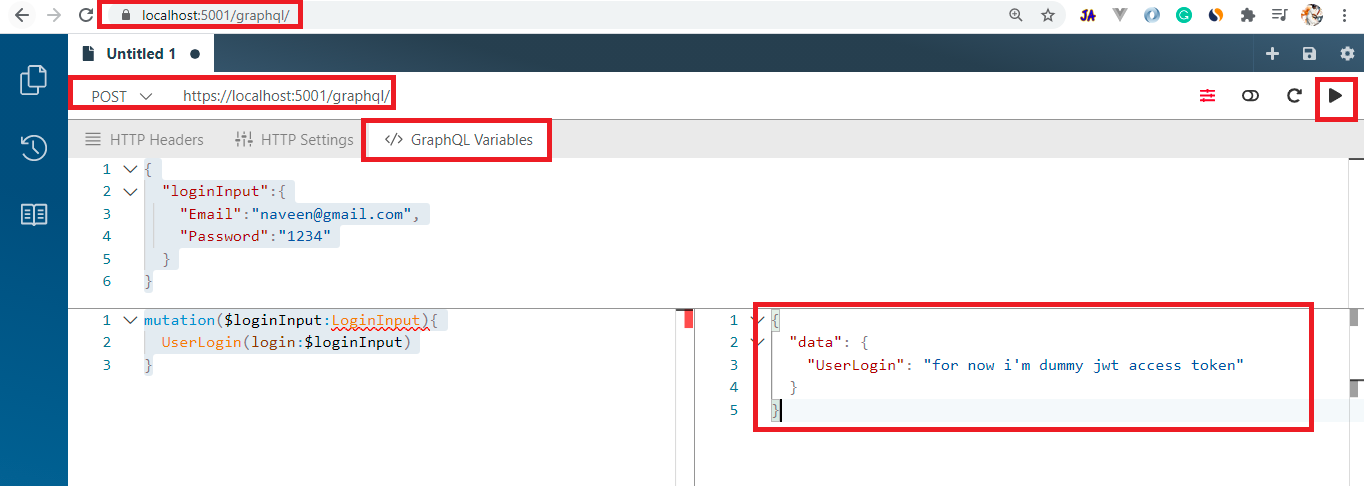
services.AddGraphQLServer() .AddMutationType<MutationObjectType>();Now run the application to test the login user mutation resolver.
The above image displaying an error, this error occurs when we try to access the GraphQL endpoint. So from the error, we have to understand that our GraphQL endpoint expecting a Query object. But till now we don't have the necessity to create a Query object. So to fix the issue we will create a Query object with one dummy resolver method.
GraphQLCore/Query.cs:
namespace HotChoco.GprahQL.Jwt.Auth.GraphQLCore
{
public class Query
{
public string Welcome(){
return "Welcome to everyone";
}
}
}
GraphQLModel/ObjectType/QueryObjectType.cs:
using HotChoco.GprahQL.Jwt.Auth.GraphQLCore;
using HotChocolate.Types;
namespace HotChoco.GprahQL.Jwt.Auth.GraphQLModel.ObjectType
{
public class QueryObjectType: HotChocolate.Types.ObjectType<Query>
{
protected override void Configure(IObjectTypeDescriptor<Query> descriptor)
{
descriptor.Field(_ => _.Welcome()).Name("Welcome").Type<StringType>();
}
}
}
Startup.cs:
services.AddGraphQLServer() .AddQueryType<QueryObjectType>() .AddMutationType<MutationObjectType>();Now run the application, we can observe our issue get resolved. Now let's test our login user mutation resolver.
GraphQL Mutation Syntax: (Mutation Part)
mutation($loginInput:LoginInput){
UserLogin(login:$loginInput)
}
- The '$loginInput' is variable and its type is 'LoginInput'. This 'LoginInput' type is nothing but the type of the c# class model that is using as payload for UserLogin resolver in Mutation.
- The 'UserLogin' is our field name where our UserLogin method registered.
- The 'login' variable name must match with the name specified in the 'Argument' extension method on registering the field.
{
"loginInput":{
"Email":"naveen@gmail.com",
"Password":"1234"
}
}Install JWT NuGet Package:
To use JWT need to install 'System.IdentityModel.Tokens.Jwt' NuGet package.
.Net CLI Command: dotnet add package System.IdentityModel.Tokens.Jwt
Package Manager Command: Install-Package System.IdentityModel.Tokens.Jwt
Instance Of JwtSecurityToken:
Instance Of System.IdentityModel.Tokens.Jwt.JwtSecurityToken used for preparing the object that creates JWT. JwtSecurityToken instance defined with multiple overloaded constructors that expects input values to prepare JWT. Here we going to use one of the overloaded constructors which more simple and provide more user options.
JwtSecurityToken Constructor:(One of the overloaded constructor)
public JwtSecurityToken( string issuer = null, string audience = null, IEnumerable<Claim> claims = null, DateTime? notBefore = null, DateTime? expires = null, SigningCredentials signingCredentials = null);
- This constructor takes all inputs of type optional parameters
- issuer parameter - if the value is not null, a {iss, 'issuer'} claim will be added, overwriting any 'iss' claim in claims if present. In most cases, issuer value will be the hosted domain(eg:- mywebsite.com).
- audience parameter - if the value is not null, a {aud, 'audience'} claim will be added, overwriting any 'aud' claim in claims if present. This value used to identify the client that consuming the protected API.
- claims parameter - this represents claims belongs to the login users.
- expires parameter - to determine the token expiration time.
- signingCredentials parameter - secured key value that used to make token to be digitally verified.
Add Token Settings To appsettings.json File:
Let's fetch a few configurations of authentication token from the appsettings.json file. One of the main settings is 'key' which some random key for the application(this key will used for generating a digital signature for JWT, as suggestion you can generate this key using some SHA512 algorithm or you can also generate from online providers but you need secure this from exposures).
appsettings.json:
{
"TokenSettings":{
"Issuer":"localhost:5001",
"Audience":"API",
"Key":"MySecuredKey12345678910MySecuredKey12345678910"
}
}
- Issuer - the setting is an optional setting token generation, by adding it gives more verification for the token. Mostly its value represents the domain of the token generation code(any value can be assigned recommended is domain)
- Audience - the setting is an optional setting token generation, by adding it makes token more verified and trusted. Usually, it represents the client consuming the authentication token, which means this appropriate for multiple API clients using a single authentication API then each client will be identified by it name and that name value will be assigned to Audience. But in our case, client API and authentication API are the same so I'm simply naming it as 'API'(you can assign any value but it should match on token verification on authentication which we will discuss in later steps).
- Key - the setting is mandatory for token generation, it is used as an ingredient in generating the digital signature.
Shared/TokenSettings.cs:
namespace HotChoco.GprahQL.Jwt.Auth.Models
{
public class TokenSettings
{
public string Issuer { get; set; }
public string Audience { get; set; }
public string Key { get; set; }
}
}
Now register the TokenSettings in Startup.cs file.Startup.cs:
services.Configure<TokenSettings>(Configuration.GetSection("TokenSettings"));
Update UserLogin Mutation Resolver To Generate JWT Access Token:
Now we need to update our logic to generate an access token for the authenticated user.
GraphQLCore/Mutation.cs:
public string UserLogin([Service] IOptions<TokenSettings> tokenSettings, LoginInput login)
{
var currentUser = Users.Where(u => u.Email.ToLower() == login.Email &&
u.Password == login.Password).FirstOrDefault();
if (currentUser != null)
{
var symmetricSecurityKey = new SymmetricSecurityKey(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(tokenSettings.Value.Key));
var credentials = new SigningCredentials(symmetricSecurityKey, SecurityAlgorithms.HmacSha256);
var jwtToken = new JwtSecurityToken(
issuer: tokenSettings.Value.Issuer,
audience: tokenSettings.Value.Audience,
expires: DateTime.Now.AddMinutes(20),
signingCredentials: credentials
);
string token = new JwtSecurityTokenHandler().WriteToken(jwtToken);
return token;
}
return string.Empty;
}
- (Line: 1) The signature of our resolver method is changed. Injecting 'TokenSettings' as the first parameter. Here we used the 'HotChocolate.Service' attribute for injection into the method.
- (Line: 8-9) Using our secret with security algorithm like 'Sha256' generating digital signature credentials.
- (Line: 11-16) Initializing JwtSecrutToken instance by providing all the user information into it.
- (Line: 18) Generating access token which is encrypted information of the user.
GraphQLModel/ObjectType/MutationObjectType.cs:
descriptor.Field(_ => _.UserLogin(default,default))
.Type<StringType>()
.Name("UserLogin")
.Argument("login", a => a.Type<LoginInputObjectType>());
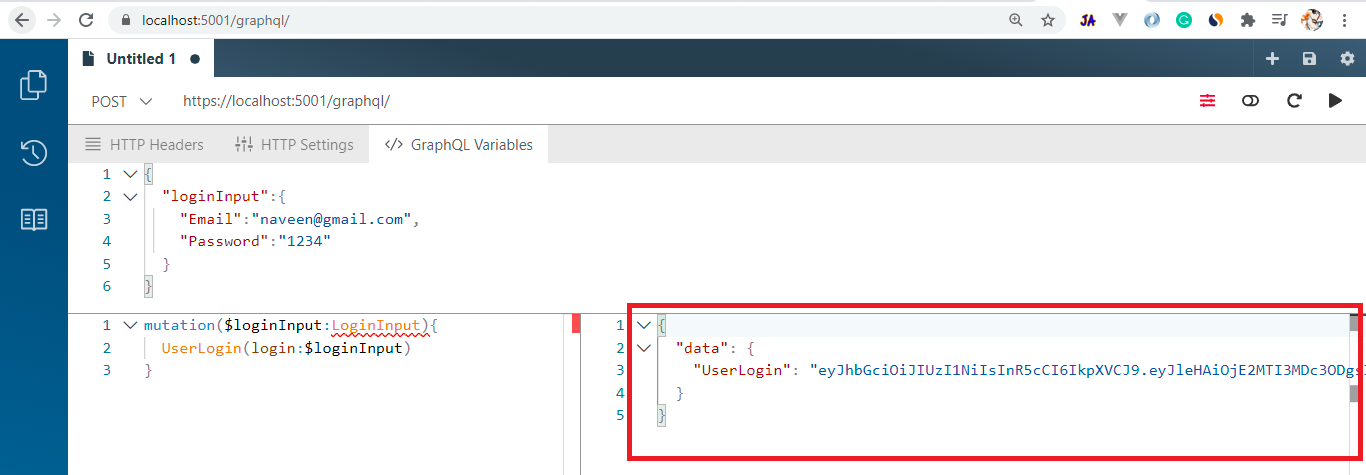
Now test our mutation endpoint we will receive an authenticated user access token as below.That's all about generating the JWT access token in the GraphQL endpoint. In the next part, we will discuss validating the JWT token and after that, we will learn about the implementation of GraphQL authorization techniques.Video Session:
Support Me!
Buy Me A Coffee
PayPal Me
Wrapping Up:
Hopefully, I think this article delivered some useful information on generating the JWT access token in the Hot Chocolate GraphQL endpoint. I love to have your feedback, suggestions, and better techniques in the comment section below.

Is the source code available on GitHub
ReplyDeleteHi,
Deletehttps://github.com/Naveen512/Hotchoco.GraphQL.Jwt