Part-2 Adding New User Into Database And Generating Custom JWT Token - (Blazor WebAssembly Standalone App Google Authentication)
Part-1 implemented sample to work with Google authentication into a Blazor WebAssembly standalone application. Now in this article, we will create user records into our database on users authenticated into our application using a Google account. Also, create a custom JWT for our secured endpoint. Because token given by google for our blazor web assembly application can't be used against our own secured endpoint. So while saving the user record into our database we will also generate the JWT token.
Now let's create one class 'AccountLogic.cs' and one interface 'IAccountLogic.cs' to implement our core logic for adding the user to the database and then generating the JWT token.
Configure Email Scope:
By default, the Blazor WebAssembly template requests scope like 'openid', 'profile'. Now we have to add one more additional scope like 'email'.
If you observe after login with a google account, the user email is not sent by google as a claim to our blazor application.
So to add user record we should have the email address, so for that let's add a new scope like 'email', which will give us user email address as one of the claims in google response token. So in 'AddOidcAuthentication' method, we have to configure the email scope.
Program.cs:
builder.Services.AddOidcAuthentication(options =>
{
// Configure your authentication provider options here.
// For more information, see https://aka.ms/blazor-standalone-auth
builder.Configuration.Bind("Local", options.ProviderOptions);
options.ProviderOptions.DefaultScopes.Add("email");
});Create A .Net5 Web API And Configure Entity Framework Core:
So to register users into the database and creating a custom jwt token that is used to secure endpoints, so let's create a .Net5 Web API.
Install entity framework core NuGet.
Package Manager:
Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore -Version 5.0.5
.Net CLI:
dotnet add package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore --version 5.0.5
Install SQL extension for entity framework core NuGet.
Package Manager:
Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer -Version 5.0.5
.Net CLI
dotnet add package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer --version 5.0.5
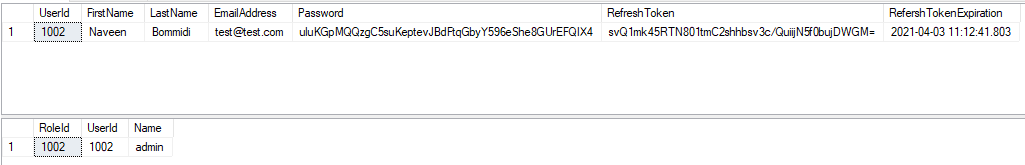
Design tables like 'User' and 'UserRoles' like below.Now we will implement database context to establish a connection with the database.
Data/Entities/User.cs:
using System;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace BwasmAPI.GoogleAuth.Data.Entities
{
public class User
{
[Key]
public int UserId { get; set; }
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public string EmailAddress { get; set; }
public string Password { get; set; }
public string RefreshToken { get; set; }
public DateTime? RefershTokenExpiration { get; set; }
}
}
Data/Entities/UserRoles.cs:
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace BwasmAPI.GoogleAuth.Data.Entities
{
public class UserRoles
{
[Key]
public int RoleId { get; set; }
public int UserId { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}
}
Data/AuthContext.cs:
using BwasmAPI.GoogleAuth.Data.Entities;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace BwasmAPI.GoogleAuth.Data
{
public class AuthContext : DbContext
{
public AuthContext(DbContextOptions<AuthContext> options) : base(options)
{
}
public DbSet<User> User { get; set; }
public DbSet<UserRoles> UserRoles { get; set; }
}
}
Add the connectionstring in json config file.appsettings.Development.json:
"ConnectionStrings": {
"AuthContext":"Your_Connection_String"
}
Now register 'AuthContext' in the 'Startup.cs'.Startup.cs:
services.AddDbContext<AuthContext>(options =>
{
options.UseSqlServer(Configuration.GetConnectionString("AuthContext"));
});
Create EndPoint To Register Google User And Return JWT Token As Response:
Our target is to create an endpoint to register the google user. So that we can save google authenticated users into the database. Now google token can't be used against our API application, so to make our API authenticated we will generate the JWT token. So for our register endpoint, we will return our custom JWT token as a response.
Let's configure settings for the JWT token in 'appsettings.Development.json'.
appsettings.Development.json:
"TokenSettings":{
"Issuer":"localhost:6001",
"Audience":"localhost:5001",
"Key":"SomeRandomlyGeneratedStringSomeRandomlyGeneratedString"
}
- Issuer value will be used as 'iss' claim in JWT. The value should be like the domain of the 'API' that generates jwt.
- Audience value will be used as 'aud' claim in JWT. The value should be like the domain of the client application that consumes the API.
- The key value should be some randomly generated string.
Shared/TokenSettings.cs:
public class TokenSettings
{
public string Issuer { get; set; }
public string Audience { get; set; }
public string Key { get; set; }
}
Register the token settings in the 'Startup.cs'.Startup.cs:
services.Configure<TokenSettings>(Configuration.GetSection("TokenSettings"));
Let's create models for the request and response of our API. So let's create a folder like 'Models' and then add files like 'RegisterGoogleUserModel.cs'(request model) and 'TokenResponseModel.cs'(response model).
Models/RegisterGoogleUserModel:
namespace BwasmAPI.GoogleAuth.Models
{
public class RegisterGoogleUserModel
{
public string FirstName{get;set;}
public string LastName{get;set;}
public string Email{get;set;}
}
}
Models/TokenResponseModel:
namespace BwasmAPI.GoogleAuth.Models
{
public class TokenResponseModel
{
public string JwtToken { get; set; }
}
}
Now let's create one class 'AccountLogic.cs' and one interface 'IAccountLogic.cs' to implement our core logic for adding the user to the database and then generating the JWT token.
So first let's create the interface with a method definition as below.
Logics/IAccountLogic.cs:
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using BwasmAPI.GoogleAuth.Models;
namespace BwasmAPI.GoogleAuth.Logics
{
public interface IAccountLogic
{
Task<TokenResponseModel> RegisterGoogleUser(RegisterGoogleUserModel googleUserModel);
}
}
Now create the 'AccountLogic.cs' and inject the required settings.Logics/AccountLogic.cs:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IdentityModel.Tokens.Jwt;
using System.Linq;
using System.Security.Claims;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using BwasmAPI.GoogleAuth.Data;
using BwasmAPI.GoogleAuth.Data.Entities;
using BwasmAPI.GoogleAuth.Models;
using BwasmAPI.GoogleAuth.Shared;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Options;
using Microsoft.IdentityModel.Tokens;
namespace BwasmAPI.GoogleAuth.Logics
{
public class AccountLogic:IAccountLogic
{
private readonly AuthContext _authContext;
private readonly TokenSettings _tokenSettings;
public AccountLogic(AuthContext authContext,
IOptions<TokenSettings> tokenSettings)
{
_authContext = authContext;
_tokenSettings = tokenSettings.Value;
}
}
}
Now let's implement the logic for adding the user into the database. So let's create a private method like 'CreateNewUser'.Logics/AccountLogic.cs:
private async Task CreateNewUser(
RegisterGoogleUserModel googleUserModel,
User user,
List<UserRoles> userRoles)
{
user = new User
{
EmailAddress = googleUserModel.Email,
FirstName = googleUserModel.FirstName,
LastName = googleUserModel.LastName,
};
_authContext.User.Add(user);
await _authContext.SaveChangesAsync();
UserRoles defaultRole = new UserRoles
{
Name = "admin",
UserId = user.UserId
};
_authContext.UserRoles.Add(defaultRole);
await _authContext.SaveChangesAsync();
userRoles.Add(defaultRole);
}
- Here we are adding our google authenticated user to the database along with the default roles.
Logics/AccountLogic.cs:
private string GetJWTAuthKey(List<UserRoles> roles)
{
var securtityKey = new SymmetricSecurityKey(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(_tokenSettings.Key));
var credentials = new SigningCredentials(securtityKey, SecurityAlgorithms.HmacSha256);
var claims = new List<Claim>();
if ((roles?.Count ?? 0) > 0)
{
foreach (var role in roles)
{
claims.Add(new Claim(ClaimTypes.Role, role.Name));
}
}
var jwtSecurityToken = new JwtSecurityToken(
issuer: _tokenSettings.Issuer,
audience: _tokenSettings.Audience,
expires: DateTime.Now.AddMinutes(30),
signingCredentials: credentials,
claims: claims
);
return new JwtSecurityTokenHandler().WriteToken(jwtSecurityToken);
}
- Here generating the JWT with the help of token settings, user claims, digital signature, etc.
Logics/AccountLogic.cs:
public async Task<TokenResponseModel> RegisterGoogleUser(RegisterGoogleUserModel googleUserModel)
{
var user = _authContext.User.Where(_ => _.EmailAddress == googleUserModel.Email).FirstOrDefault();
List<UserRoles> userRoles = new List<UserRoles>();
if (user == null)
{
// create new user and default roles
await CreateNewUser(googleUserModel, user, userRoles);
}
if (userRoles.Count == 0)
{
userRoles = _authContext.UserRoles.Where(_ => _.UserId == user.UserId).ToList();
}
return new TokenResponseModel
{
JwtToken = GetJWTAuthKey(userRoles)
};
}
Register 'IAccountLogic' and 'AccountLogic' in the 'Startup.cs'Startup.cs:
services.AddScoped<IAccountLogic,AccountLogic>();So to set up our endpoint let's create a new controller like 'AccountController.cs'.
Controllers/AccountController.cs:
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using BwasmAPI.GoogleAuth.Logics;
using BwasmAPI.GoogleAuth.Models;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace BwasmAPI.GoogleAuth.Controllers
{
[ApiController]
[Route("[controller]")]
public class AccountController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly IAccountLogic _accountLogic;
public AccountController(IAccountLogic accountLogic)
{
_accountLogic = accountLogic;
}
[HttpPost]
[Route("register-google-user")]
public async Task<IActionResult> RegisterGoogleUser(RegisterGoogleUserModel googleUserModel)
{
var result = await _accountLogic.RegisterGoogleUser(googleUserModel);
return Ok(result);
}
}
}
Enable Cors In API:
To consume API by our Blazor WebAssembly application we need to enable cors.
Startup.cs:(ConfigureServices Method)
services.AddCors(options =>
{
options.AddPolicy(name: "corsService",
builder =>
{
builder.AllowAnyOrigin();
builder.AllowAnyHeader();
builder.AllowAnyMethod();
});
});
Startup.cs:(Configure Method)
app.UseCors("corsService");
- Add the 'UseCors' middleware after the 'UseRouting()' middleware.
Create A Typed Client(HttpClient) To Consume Register Endpoint From Our Blazor App:
Now we have to consume the register API in our Blazor application and also need to receive the JWT token.
NOTE: If we recall in previous steps in API configure with request model(RegisterGoogleUserRequestModel.cs) and response model(TokenResponseModel.cs). So in our blazor webAssembly applications also need to have the same exact classes for invoking API. So here I'm skipping them in the blog.
So to consume API we will use the Typed Client HttpClient technique. Let's create a type client class like 'AppAuthClient.cs'.
ApiCalls/AppAuthClient.cs:
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Net.Http.Json;
using System.Text;
using System.Text.Json;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using BWasm.google.Auth.Models;
namespace BWasm.google.Auth.ApiCalls
{
public class AppAuthClient
{
private HttpClient _httpClient;
public AppAuthClient(HttpClient httpClient)
{
_httpClient = httpClient;
}
public async Task<TokenResponseModel> RegisterGoogleUser(RegisterGoogleUserRequestModel googleUserRequestModel)
{
var postData = new StringContent(JsonSerializer.Serialize(googleUserRequestModel),Encoding.UTF8,"application/json");
var response = await _httpClient.PostAsync("/Account/register-google-user", postData);
response.EnsureSuccessStatusCode();
return await response.Content.ReadFromJsonAsync<TokenResponseModel>();
}
}
}
- So here invoking endpoint like '/Account/register-google-user'. Here post payload contains user information like 'firstname', 'lastname', and 'email' from the google token. Here we expect the custom JWT token of our API as the response.
Package Manager:
Install-Package Microsoft.Extensions.Http -Version 5.0.0
.Net CLI:
dotnet add package Microsoft.Extensions.Http --version 5.0.0
Now register our 'AppAuthClient.cs' in startup.cs along with our domain API.Startup.cs:
builder.Services.AddHttpClient<AppAuthClient>(options => {
options.BaseAddress = new Uri("https://localhost:6001");
});
Implement AccountClaimsPrincipalFactory In Blazor App:
Now we have to implement AccountCliamsPrincipalFactory so that we can invoke the register API. So let's create a folder like 'Providers' and then add a new class like 'CustomAccountFactory.cs'
Providers/CustomAccountFactory.cs:
using System.Linq;
using System.Security.Claims;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using BWasm.google.Auth.ApiCalls;
using BWasm.google.Auth.Models;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components.WebAssembly.Authentication;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components.WebAssembly.Authentication.Internal;
namespace BWasm.google.Auth.Providers
{
public class CustomAccountFactory
: AccountClaimsPrincipalFactory<RemoteUserAccount>
{
private readonly AppAuthClient _appAuthClient;
public CustomAccountFactory(IAccessTokenProviderAccessor accessor,
AppAuthClient appAuthClient
) : base(accessor)
{
_appAuthClient = appAuthClient;
}
public async override ValueTask<ClaimsPrincipal> CreateUserAsync(
RemoteUserAccount account, RemoteAuthenticationUserOptions options)
{
var initialUser = await base.CreateUserAsync(account, options);
try
{
if (initialUser.Identity.IsAuthenticated)
{
var googleUser = new RegisterGoogleUserRequestModel
{
Email = initialUser.Claims.Where(_ => _.Type == "email").Select(_ => _.Value).FirstOrDefault(),
FirstName = initialUser.Claims.Where(_ => _.Type == "given_name").Select(_ => _.Value).FirstOrDefault(),
LastName = initialUser.Claims.Where(_ => _.Type == "family_name").Select(_ => _.Value).FirstOrDefault()
};
var response = await _appAuthClient.RegisterGoogleUser(googleUser);
((ClaimsIdentity) initialUser.Identity).AddClaim(
new Claim("APIjwt", response.JwtToken)
);
}
}
catch
{
initialUser = new ClaimsPrincipal(new ClaimsIdentity());
}
return initialUser;
}
}
}
- (Line: 12) Inheriting 'AccountCliamsPrincipalFactory<RemoteUserAccount>'.
- (Line: 16) Injected our typed client 'AppAuthClient'.
- (Line: 30-36) Making payload object like 'RegisterGoogleUserRequestModel'. The data loaded into it from google authenticated claims.
- (Line: 38) Invoking the user registration API.
- (LIne: 40-42) Updating use claims. Added our API jwt token as one of the user claims. So by using the claim we will try to access our secure endpoints
Program.cs:
builder.Services.AddOidcAuthentication<RemoteAuthenticationState,
RemoteUserAccount>(options =>
{
builder.Configuration.Bind("Local", options.ProviderOptions);
options.ProviderOptions.DefaultScopes.Add("email");
})
.AddAccountClaimsPrincipalFactory<RemoteAuthenticationState,
RemoteUserAccount, CustomAccountFactory>();
Now run both API and our blazor web assembly application and test the google user registration.
Create Secured Endpoint In Our API Project:
After login, we will have our custom JWT token. So to test the Jwt token we will create a secured endpoint in the API project.
First, let's enable the token verification service in 'Startup.cs'.
Startup.cs:
services.AddAuthentication(JwtBearerDefaults.AuthenticationScheme)
.AddJwtBearer(options =>
{
var tokenSettings = Configuration
.GetSection("TokenSettings").Get<TokenSettings>();
options.TokenValidationParameters = new TokenValidationParameters
{
ValidIssuer = tokenSettings.Issuer,
ValidateIssuer = true,
ValidAudience = tokenSettings.Audience,
ValidateAudience = true,
IssuerSigningKey = new SymmetricSecurityKey(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(tokenSettings.Key)),
ValidateIssuerSigningKey = true,
};
});
Now register the authentication middleware just above the authorization middleware.Startup.cs:
app.UseAuthentication();Now let's create an example secured endpoint for our testing.
Controllers/AccountController.cs:
[Authorize]
[HttpGet]
[Route("cities")]
public IActionResult Cities()
{
return Ok(new List<string>{"Hyderabad","Mumbai","Bangalore"});
}
Consume Secured API From Our Blazor WebAssembly Application:
Now let's write the logic in our typed client class to consume the secured endpoint.
ApiCalls/AppAuthClient.cs:
public async Task<List<string>> GetCities(string token)
{
_httpClient.DefaultRequestHeaders.Authorization = new AuthenticationHeaderValue("bearer", token);
return await _httpClient.GetFromJsonAsync<List<string>>("/Account/cities");
}
- Here invoking the secured endpoint by adding our jwt token as an authorization header value.
Pages/Index.razor:
@page "/"
@inject BWasm.google.Auth.ApiCalls.AppAuthClient _authClient;
<h1>Hello, world!</h1>
<AuthorizeView>
<ul>
@foreach (var item in cities)
{
<li>@item</li>
}
</ul>
</AuthorizeView>
@code{
public List<string> cities = new List<string>();
[CascadingParameter]
private Task<AuthenticationState> authenticationState { get; set; }
protected override async Task OnInitializedAsync()
{
var authState = authenticationState.Result;
if (authState.User.Identity.IsAuthenticated)
{
string apiToken = authState.User.Claims.Where(_ => _.Type == "APIjwt").Select(_ => _.Value).FirstOrDefault();
cities = await _authClient.GetCities(apiToken);
}
}
}So that's all about registering the google user and generating the jwt token.Video Session:
Support Me!
Buy Me A Coffee
PayPal Me
Wrapping Up:
Hopefully, I think this article delivered some useful information about adding google users to the database and generating JWT Blazor Webassembly Standalone Application. I love to have your feedback, suggestions, and better techniques in the comment section below.



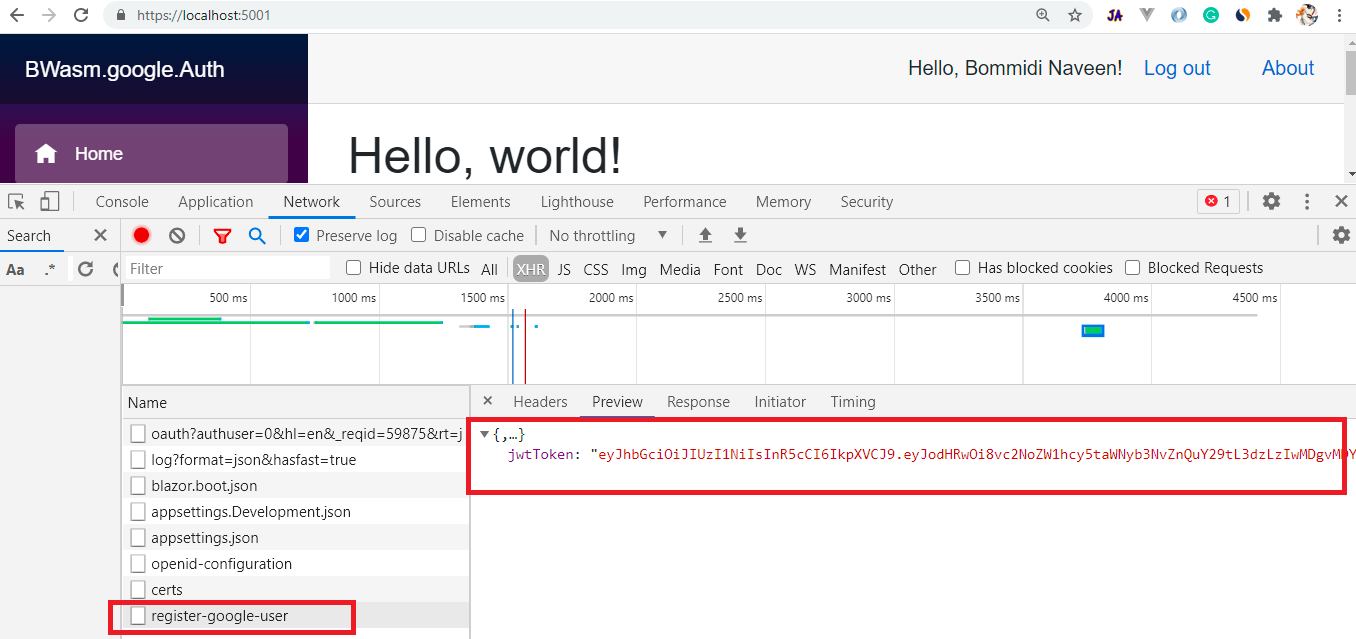
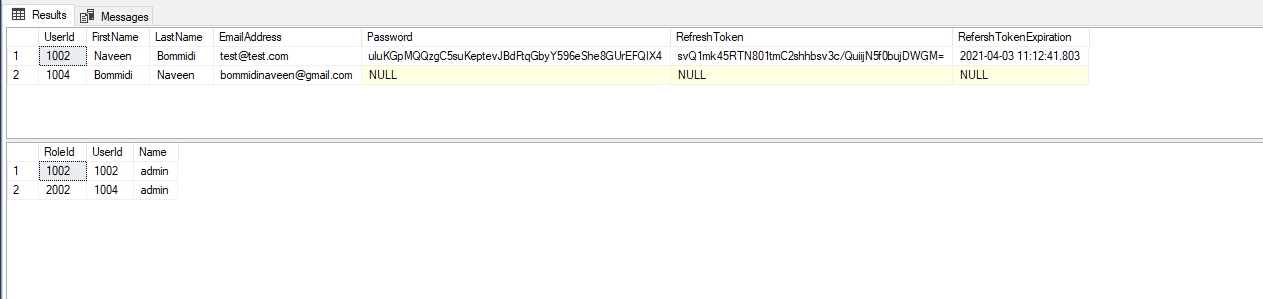

I think there is a problem with the way the client is sending the information to the backend. Without the Google token being sent, how can the server trust that RegisterGoogleUserModel is not a fraud? It seems that anyone could send a POST to the server and get a JWT.
ReplyDeleteYes, you can get the token that way. There must be a way to validate in the WebAPI.
Delete